Le Fokker D. VII
English Translation
 |
Le Fokker D. VII était le meilleur avion de combat allemand en service à la fin de la 1ère guerre mondiale. L'Allemagne a produit environ 1.700 D. VII au cours de l'été et l'automne de 1918 Après l'armistice, il a été expressément demandée à l'Allemagne de livrer tous les D. VII aux Alliés
Cet avion a permis à Fokker de rétablir sa réputation qui avait quelque peu souffert des problèmes suite aux médiocres performances d’une série d’une série de biplans médiocres
Après la 1ère guerre mondiale cet avions fut utilisé par de nombreux autres pays
Histoire
Le D. VII a été construit par trois usines – Fokker, Albatros et une filiale d’Albatros l’OAW.
Au cours de la 1ère guerre mondiale Anthony Fokker Néerlandais d’origine construisit des avions en Allemagne, dans son usine située sur l'aérodrome de Johannisthal, près de Berlin. Celle-ci fut transférée en 1913 à Schwerin. Un grand nombre d’ avions des différents types ont été conçus et construits là-bas, parmi lesquels le fameux "Eindecker et le Dr. I triplan. Mais ces avions ont été suivis par une série d’avions aux performances médiocres
A l’ automne 1917, les allemands ont perdu la supériorité aérienne, aussi en Allemagne l’Idflieg (Inspektion der Fliegertruppen Inspection générale de l'aviation) fixe rapidement une date pour une compétition concernant les avions de combat, avec l'objectif de remplacer les avions en ligne suite à l'apparition du Sopwith Camel et du SPAD XIII Avec ces chasseurs alliés tous les avions allemands de chasse sont devenus obsolètes et l'entrée en guerre des Etats-Unis exige une augmentation du taux de production et les productions des moteurs demandent a être standardisée. Le chasseur le plus moderne est le Fokker FI (triplan) arrivé sur le front pendant le mois d'août 1917, mais il avait eu des problèmes notamment avec la construction des ailes. Pour rattraper ce retard le plus rapidement possible, un appel d'offres sur le développement d'un nouveau chasseur été lancé Il s’agira d’un chasseur de classe D. En effet à l’automne 1917, les escadrilles de chasse allemands avaient perdu la supériorité aérienne au détriment des avions alliés. L'entrée en guerre des Etats-Unis exigea une augmentation des cadences de production des avions et moteurs qu'on voulait obtenir par une plus grande standardisation. Afin d'atteindre le plus rapidement possible ce but, un appel d'offre à grande envergure portant sur le développement d'un nouveau chasseur standard fut lancé. Un des problèmes majeurs des industriels était la pénurie de nouveaux moteurs plus puissants. Une augmentation des performances était uniquement possible par des conceptions ingénieuses visant par exemple à réduire le poids.
Ainsi, le Fokker D VII marque le retour Fokker au premier plan car en 1917, les Allemands ont besoin d'un remplacement pour le Fokker triplan DR.1 pour contrer la supériorité aérienne alliée Fokker inscrit au concours avec un nouveau chasseur, le V-11
Fokker D. VII, a été conçu par Reinhold Platz ingénieur et fabricant d'aéronefs travaillant pour Fokker de Flug zugwerke Après la 1e Guerre Mondiale Platz deviendra ingénieur en che de l'usine de Fokker à Amsterdam
Le prototype de ce qui allait devenir le Fokker D. VII, a été construit en Décembre 1917 dans l'usine Junker à Schwerin. La désignation de ce type a été V.11, (V11 pour Versuchsmachine no. 11 ou avion expérimental n ° 11)
Au début de 1918, (du 21 Janvier au 12 Février 1918) les epreuves de selection pour un chasseur de classe D (D - monoplace armé avion, propulsé par un moteur de plus de 150 ch) ont lieu à Berlin-Adlershof. Dans cette compétition, les pilotes allemands effectuent les tests sur ces nouveaux chasseurs avant de choisir le vainqueur. Dans le cadre de ce concours, nous trouvons les avions suivants
Albatros D. Va
Aviatik D. III
Fokker V.11
Fokker V.13 / I mu par un moteur Oberursel de 110 CV il serait le père duD.VII .2 construits
Fokker V.13/II
Fokker V.17
Fokker V.18
Fokker Dr.I
Pfalz D. IIIa
Pfalz D. VI
Pfalz D. VII
Roland D. VI
Roland D. IX
Rumpler D
Schutte-Lanz D. III
Siemens Schuckert D. III
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Pfalz D III |
Fokker V13 |
Fokker V13 II |
Fokker V17 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Fokker V 18 |
Pfalz D |
Pfalz D VII |
Roland D VI |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rumpler D |
Schutte-Lanz D. III |
Siemens Schuckert D. III |
Aviatik D. III |
 |
| Albatros D. Va |
Dans cette compétition, le Fokker V.11 est sorti vainqueur, et a été désigné D. VII, mais une partie du succès de Fokker vient aussi des bonnes relations entretenues avec plusieurs des principaux pilotes de chasse allemand, dont Manfred Von Richthofen.
Pour l'anecdote comme le prototype V11 n’avait pas obtenu d'assez bons résultats, par manque de maniabilité. Fokker a du reconstruire l'appareil à mi-concours pour produire le prototype vainqueur
Les premiers avions de production ont été testés en Mars, et adopté avec une seule modification
Les Allemands comprennent rapidement que Fokker n'a pas la capacité de produire tous ces chasseurs afin d’honorer la commande même après l’annulation de la commandes des avions d’entrainement AEG C. IV en cours de construction sous licence Pour résoudre ce problème, OAW Ostdeutsche Albatros Wercke et Albatros reçoivent des contrats pour construire les D VII sous licence en reversant à Fokker 5%. du prix final de l’avion
Sur près de 3000 avions commandés, seuls 1.000 ont été produites par Fokker.
L'avion construit par Fokker ont été nommé Fokker. D. VII par Albatros Fok. D. VII (Alb.) et par Ostdeutsche Albatros Wercke Fok. D. VII (O.A.W.) Les avions Albatros ont été construits dans l'usine de Schneidemühl
Le D. VII arrive dans les Jastas (Jagdstaffel escadrons de chasseurs en première ligne) à la fin Mars et début avril 1918.
La première unité à être équipée d'elle a été Jagdgeschwader I de Manfred Von Richthofen, bien qu'il semble que celui-ci ne l’ai pas fait des missions de guerre avec. Le nombre d'aéronefs augmente rapidement,
Mai 1918 19
Juillet 1918 407
Septembre 1918 838
Plutôt que d'équiper les unités entières avec les nouveaux avions,les Jastas (escadron de chasse), reçurent au fur et à mesure les D. VII dès que ceux-ci étaient disponibles. Les quantités de ce nouveau type ont été faibles et un seul D. VII était attribué à chaque Jasta Communément le D. VII était donné au meilleur et au plus expérimenté des pilotes. Manfred Von Richthofen a reçu son propre D. VII durant le mois d'avril, mais il préféra toujours son " lieblich" Dr.. Grace à lui de nombreux as allemand ont obtenu de grands succès avec le D. VII, mais en même temps les nouveaux pilotes, moins expérimentés ont combattus avec des avions plus anciens, et ont souffert de lourdes pertes.
À la fin de la guerre, le D. VII avait été le principal avion de 47 Jasta
Le type D VII a équipé les Jasta 4, 6, 10 et II, les Geschwader I des Jasta 12, 13, 15 et 19 les Geschwader II des Jasta 2, 26, 27 et 36 et les Geschwader III et indépendant des Jasta 5, 7, 8, 14, 16 , 17, 20, 22, 23, 24, 28, 29, 30, 32, 35, 37, 40, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 57, 58, 59 , 66, 69, 71, 79 et 80.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
Mais il est arrivé trop tard pour avoir un impact réel sur les combats. Il apparaît au cours de la 2ème bataille de la Somme (21 mars et 8 avril 1918) comme un avion d'attaque au sol.
L'Autriche a commencé la production sous licence des D. VII motorisé par des moteurs Daimler Austro en 1918 chez MAG (Magyar Általános Gépgyár - Ungarische Allgemeine Maschinenfabrik AG L la production se poursuit après la fin de la guerre, avec plus de 50 appareils complets
Description
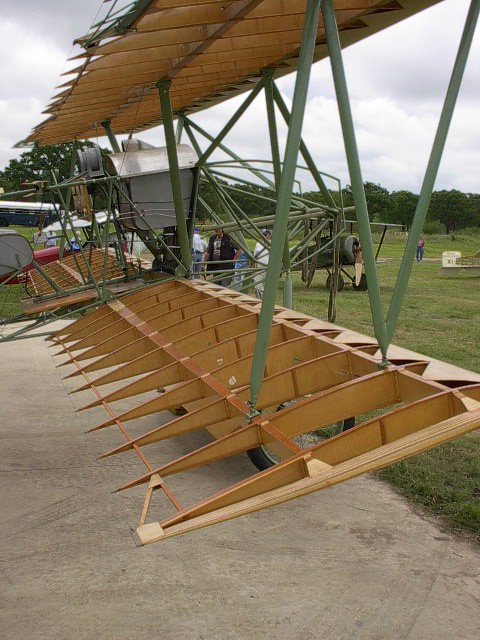
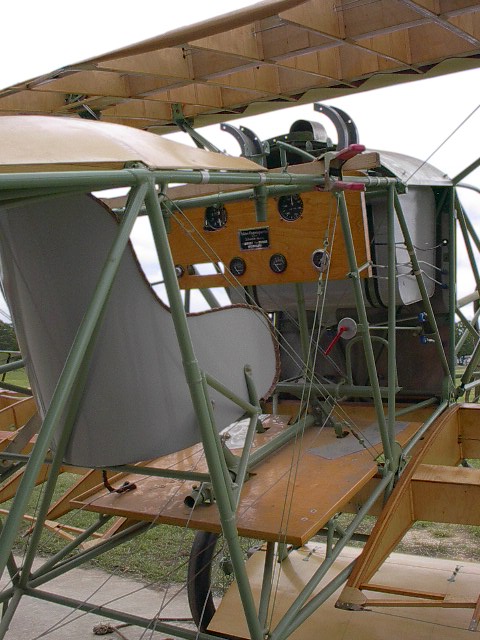
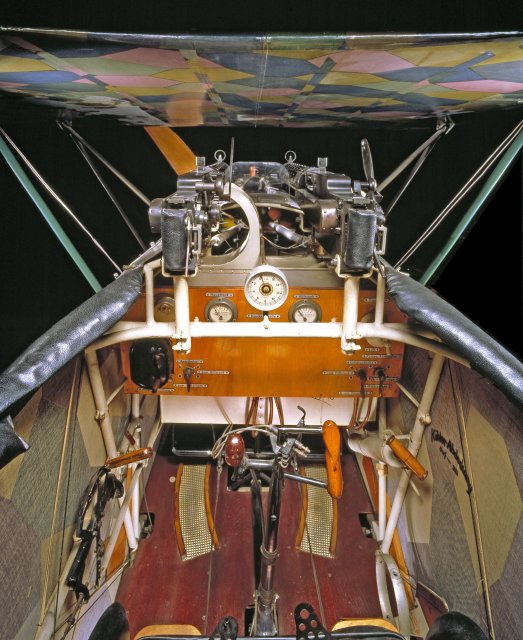
Le D VII fut construit suivant les techniques habituelles de Fokker: le fuselage et l'empennage du Biplan monoplace étaient constitués de tubes d'acier soudés et recouverts de toile tout comme les ailes construites en bois.
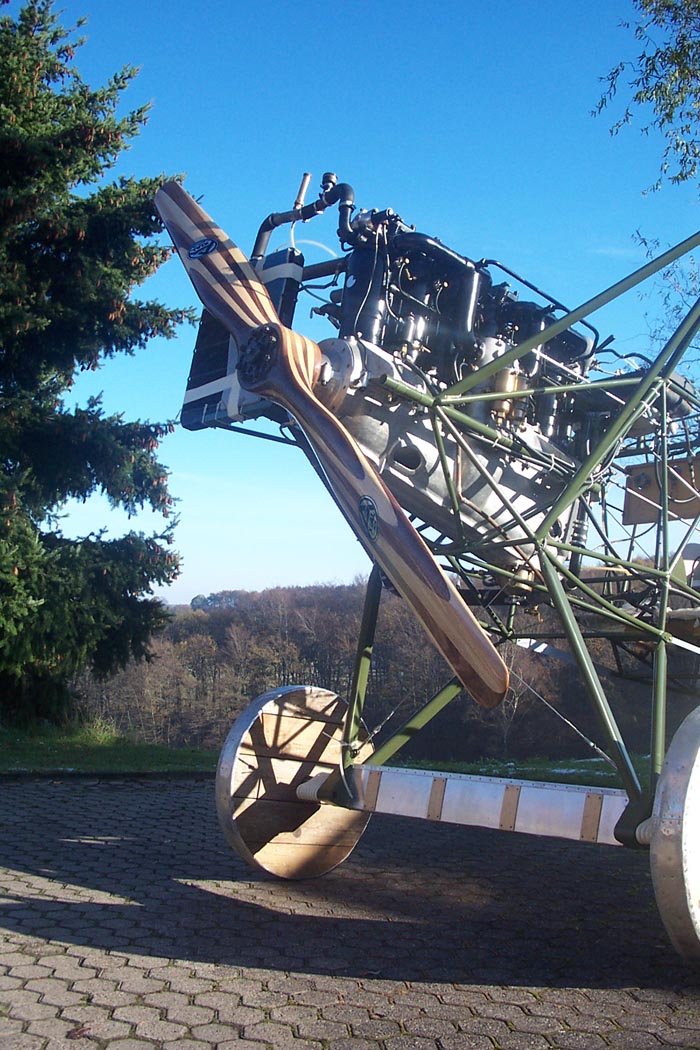
La plupart des avions étaient équipés d'un moteur en ligne Daimler D IIIa ou du nouveau moteur plus puissant BMW IIIa en fonction de la disponibilité de ce dernier. Environ un tiers de la production totale était dotée du moteur BMW dont la pleine puissance pouvait être utilisée à partir d'une altitude de 3200 m.
Ces avions reçurent la dénomination Fokker D VII F. Finalement, à partir de la fin de l'été 1918, les moteurs améliorés Daimler D III et d'autres moteurs plus puissants étaient également disponibles en quantités suffisantes pour motoriser les chasseurs produits en série.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
Le D VII se caractérisait par sa bonne vitesse ascensionnelle, sa rapidité et sa robustesse.
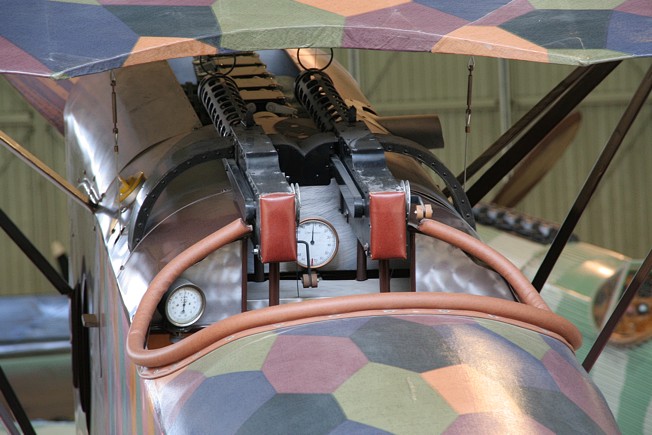
Il avait son capot spécifique et de ouïes de refroidissement du moteur car il souffrait d'un grave problème lié à la surchauffe qui fait parfois exploser les munitions, provoquant plusieurs incendies mortels L’installation d’ouies a été décidé après une série d'incendies des munitions suite à une température élevée du compartiment moteur Ce problème a été résolu en ajoutant des lamelles de refroidissement du moteur, certaines en usine d’autres directement sur le front.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
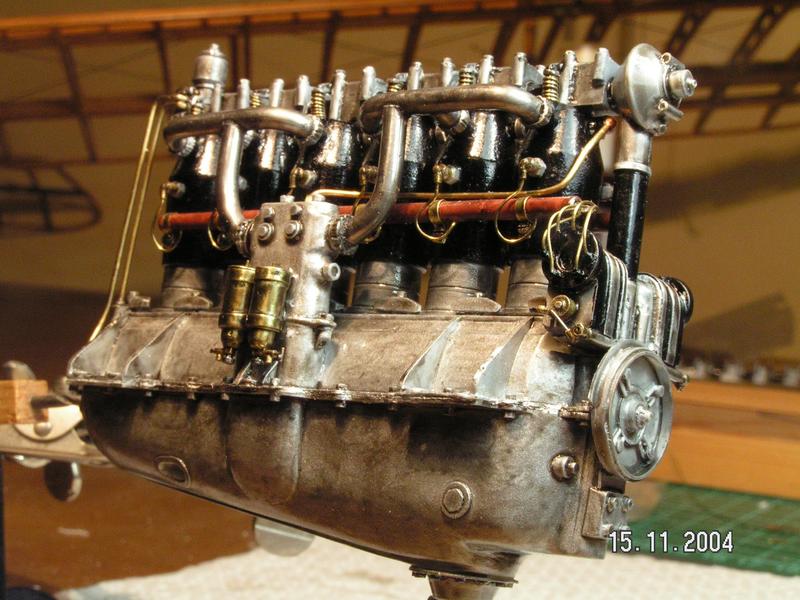
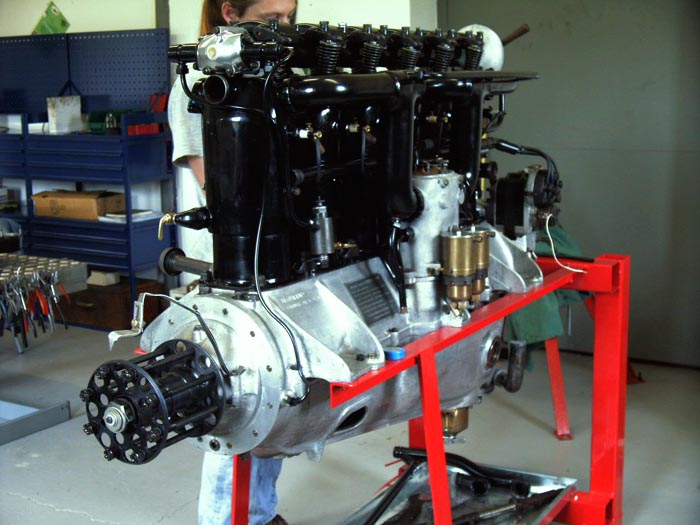
D. VII a reçu une grande variété de moteurs.
 |
 |
 |
| Mercedes D III |
BMW D III A |
Mercedes DIII aü |
Très peu utilisé l'original Mercedes D. III 160hp moteur, le remplaçant par le D. IIIaü, capable de delivrer 180-195CV et la meilleure version de l'avion a été la VIIf D., alimenté par le moteur surcompressé BMW D. IIIa moteur, capable de délivrer 185CV.
Ces avions ont été attendus par les pilotes, mais il ne furent jamais disponibles en nombre suffisant. Tous les types de D. VII ont été très populaires chez les pilotes de chasse allemands L'avion pouvait être entretenu de facon simple et il était beaucoup moins fatiguant à piloter que beaucoup de ses contemporains. À moyenne altitude, il est plus rapide et plus maniable que ses adversaires. Il accéléré rapidement en piqué tout en restant stable, ce qui en fait une bonne plate-forme d’armement.
Conclusion
Durant sa relativement brève carrière en première ligne, le D. VII s’est fait une solide réputation. Il a été le seul appareil mentionné dans la clause de l'accord d'armistice qui a demandé la cession des 2000 D VII allemands
Versions
V 11: Prototype
V 21: Prototype avec ailes coniques
V 22: Prototype helice quadripale
V 24: Prototype de 179 kW (240 ch) Benz Bz IV aü moteur
V 31: D. VII Un avion équipé d'un crochet de remorquage pour planeur V 30
V 34: D. VII développement avec 138 kW (185 ch) moteur BMW IIIa
V 35: Biplace 138 kW (185 ch) BMW IIIa
V 36: D. VII 138 kW (185 ch) BMW IIIa
V 38: Prototype Fokker C1
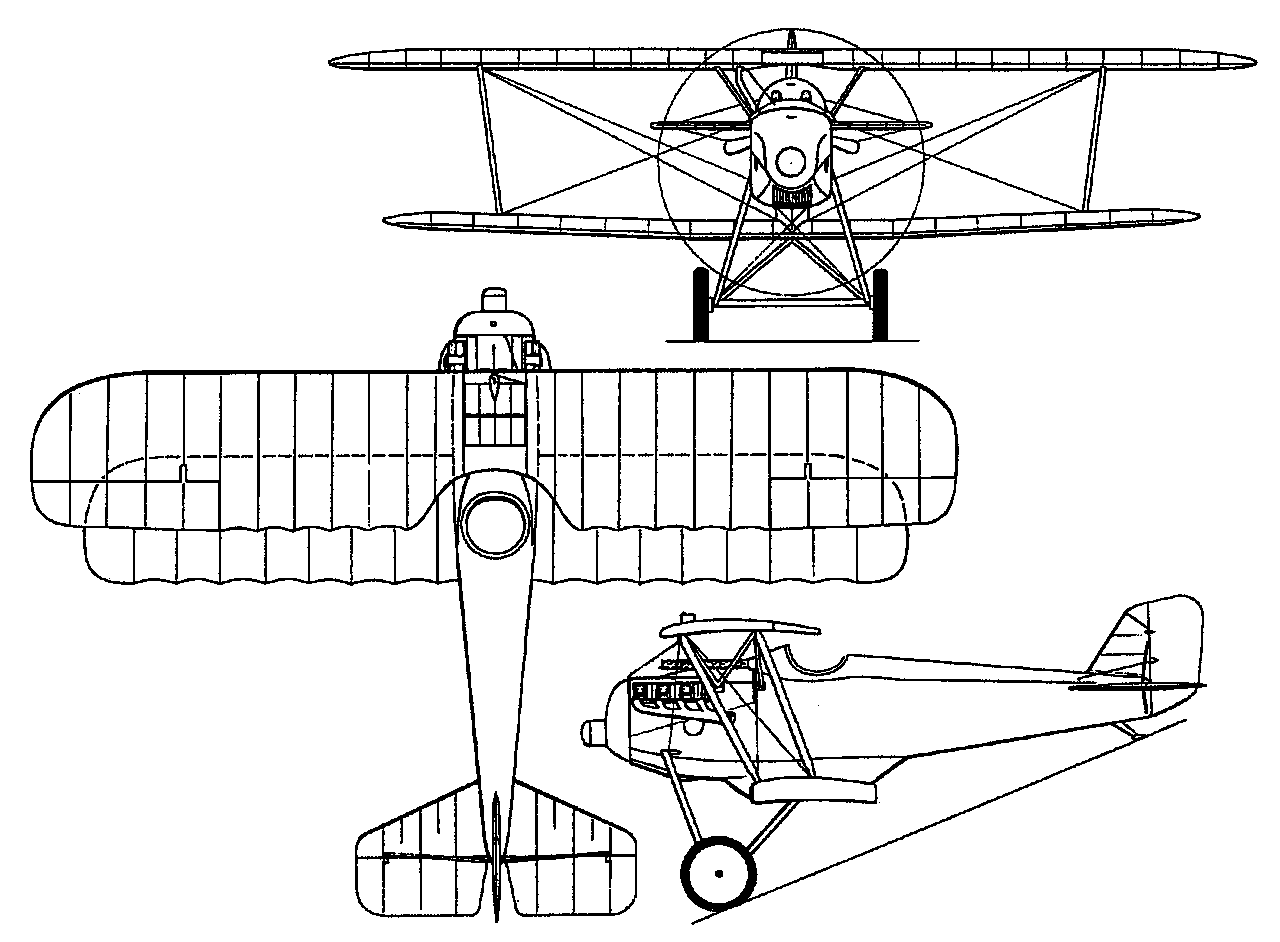
Caractéristiques
Equipage 1
Poids à vide 700 kg charge 910 kg
Dimensions
surface alaire 20.20m2
Envergure 8,9 m
Longueur 6.95m
Hauteur 2,94 m
Motorisation
Moteur refroidi par eau
V.11 Mercedes D.III 160 HP
D.VII Mercedes D.IIIaü 200 HP
D.VIIF BMW IIIa 185 HP
Vitesse maximale 190 km / h Plafond 6 000 m
Rayon d’action 350 kms
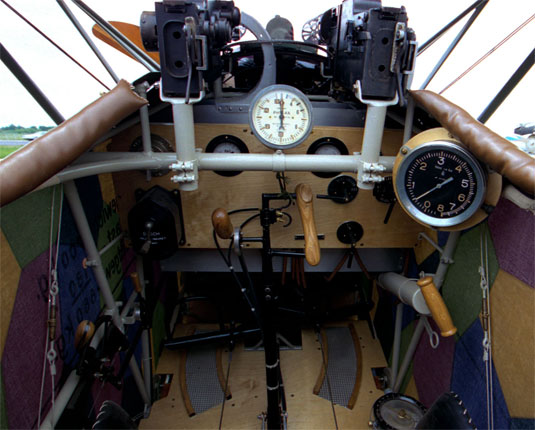
Armement 2 MG avant Spandau
Utilisateurs Users
 |
| Allemagne |
.png) |
 |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
 |
 |
 |
| Belgique |
Bulgarie |
Tchécolovaquie |
Danemark |
Finlande |
Hongrie |
Pays Bas |
 |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
 |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Lithuanie |
Pologne |
Roumanie |
URSS |
Suede |
Suisse |
USA |
Merci àThanks to AMB
The Fokker D.VII
 |
The Fokker D.VII was the best German fighter aircraft in service at the end of WW1 . Germany produced around 1,700 D.VII aircraft in the summer and autumn of 1918 After the Armistice he was specifically required Germany to surrender all the D.VIIs to the Allies
This aircraft restore Fokker’s reputation somewhat, but had still suffered from the build quality problems after the failure of the series of mediocre biplanes
After WW1 this aircraft continued widespread service with many other countries
History
The D.VII was built by three different factories - Fokker itself, Albatros and the Albatros subsiduary of OAW.
During WW1 Anthony Fokker Dutchman building aeroplanes in Germany in his factory was located at the Johannisthal airfield, near Berlin. Moved in 1913 Schwerin. A lot of different types were designed and build there, among which were the famous 'Eindecker' series, and the Dr.I triplane.But this successful aircrafts were followed by mediocre aircrafts
In autumn 1917, German fighter have lost air superiority so Germany's Idflieg (the aviation inspection section) quickly fixed a date for a Fighter Competition, with the aim of replacing the actual aircraft in action.because after appearance of the Sopwith Camel and the SPAD XIII, all German scout planes became obsolete and the entry into the war of USA demanded an increase in production rates and engines that sought greater standardization. The most modern German design, the Fokker F.I (Triplane) arrived at the Front during August of 1917 but had had problems with the construction of the wings To achieve the earliest possible this purpose, a call for tenders to large scale on the development of a new standard was launched fighter Class D. One of the major problems of industry was the shortage of new more powerful engines. An increase in performance was only possible by ingenious designs for example, to reduce weight.
So the Fokker D VII mark the return to form for Fokker In 1917 Germans need a replacement for the Fokker Dr.1 triplane to counter the air superiority of the Nieuports and the SPAD's. Fokker entered in the contest with a new fighter design, the V-11
Fokker D.VII was designed by Reinhold Platz aircraft designer and manufacturer in service of the Dutch company of Fokker Flug zugwerke After WW1.Platz became the head designer at the Fokker factory in Amsterdam
The prototype of what was to become the Fokker D.VII was built in December, 1917 in Junker factory at Schwerin. The designation for this type was V.11, (V11 for Versuchsmachine no. 11 or Experimental aircraft No. 11)
At the beginning of 1918,( 21 January to 12 February 1918 ) the first competition for D class machines (D - single-seat armed aircraft, powered by an engine of more than 150 hp )was held at Adlershof. In this competition, German pilots from the front flew in new types, to test them, and choose which one would be produced for the front. In this contest we found Albatros D.Va
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Pfalz D III |
Fokker V.13 |
Fokker V.13/II |
Fokker V.17. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Fokker V.18 |
Pfalz D |
Pfalz D.VII |
Roland D.VI |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rumpler D |
Schutte-Lanz D.III |
Siemens-Schuckert D.III |
Aviatik D.III |
 |
| Albatros D. Va |
Aviatik D.III
Albatros D Va
Fokker V.11
Fokker V.13/I
Fokker V.13/II
Fokker V.17.
Fokker V.18
Fokker Dr.I
Pfalz D.IIIa
Pfalz D.VI
Pfalz D.VII
Roland D.VI
Roland D.IX
Rumpler D
Schutte-Lanz D.III
Siemens-Schuckert D.III
In this competition the V.11 came out as the ultimate winner, and was designated D.VII but one part of Fokker’s success was due to his good relationships with many of the main German fighter pilots, including Manfred von Richthofen . for the anectode Like V.11 prototype performed reasonably well, lacked manoeuvrability. Fokker was able to rebuild the aircraft mid-contest to produce the winning prototype An early production aircraft was tested in March, and passed with only one modification
German realise that Fokker did not have the capacity to build enough aircraft for their needs, even after an order for AEG C.IV trainers being built under license was cancelled. To solve this problem, Albatros and OAW Ostdeutsche Albatros Werke were given contracts to build the D.VII under license, paying Fokker a 5% fee. Of the more than 3,000 aircraft ordered, only 1,000 were produced by Fokker. The aircraft built by Fokker were designed Fok. D.VII by Albatros Fok. D.VII(Alb.) and by Ostdeutsche Albatros Werke Fok. D.VII(O.A.W.) in the factory of Schneidemühl
D.VII appear in the Jastas (Jagdstaffel front line fighter squadrons) in late March and early April 1918.
The first unit to be equipped with it was Jagdgeschwader I, under Manfred von Richthofen, although he appears not to have flown the type in combat. The number of aircraft at the front increased rapidly,
May 1918 19
July 1918 407
September 1918 838
Rather than equip entire units with the new aircraft, Jastas received piecemeal deliveries of the D.VII as aircraft became available. Quantities of the new type were minimal and only one D.VII was assigned to each Jasta (hunting squadron) so usually the D.VII was given only to the best aces and most experienced pilots. Manfred Von Richthofen received his own D.VII during April, but he preferred his " lieblich" Dr.. As a result many German aces achieved great success in the D.VII, but at the same time less capable or new pilots were given discarded older aircraft, and suffered high casualties.
By the end of the war the D.VII had been the main aircraft for forty seven Jastas
The type equipped Jastas 4, 6, 10 and II in Geschwader I, Jastas 12, 13, 15 and 19 in Geschwader II, Jastas 2, 26, 27 and 36 in Geschwader III and independent Jastas 5, 7, 8, 14, 16, 17, 20, 22, 23, 24, 28, 29, 30, 32, 35, 37, 40, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 57, 58, 59, 66, 69, 71, 79 and 80.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
But it appeared too late in the war to have any real impact on the fighting. He appear during the 2nd Battle of the Somme ( 21 march /8 april 1918) as a ground attack aircraft.
Austria commenced license production of the D.VII powered by Austro Daimler engines late in 1918 in MÁG (Magyar Általános Gépgyár - Ungarische Allgemeine Maschinenfabrik AG in , production continuing after the end of the war, with as many as 50 aircraft complete
Description.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
The D.VII combined a conventional steel-tube fuselage with advanced internally braced cantilevered wings, constructed with plywood ribs, covered in fabric and with plywood leading edges. The ease with which the simple fuselage could be maintained was one of the reasons the type was adopted. Each had its own style of cowl and engine cooling louvres.because this aircraft suffer of one only serious problem caused by over-heating ammunition, which exploded causing several fatal fires So louvres were installed after a series of inflight fires due to the temperature of the engine compartment setting off the phosphorous ammunition in which aircraft spontaneously caught fire with disatrous results. This problem was solved by adding extra engine cooling louvers, some at the factory and some at the front line.
 |
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
Internet |
D.VII was powered by a variety of engines
 |
 |
 |
| Mercedes D III Internet |
BMW D III A Internet |
Mercedes DIII aü Internet |
.
Very few used the original Mercedes D.III 160hp engine, replacing it with the D.IIIaü, capable of producing 180-195hp.
The best version of the aircraft was the D.VIIF, powered by the over-compressed B.M.W. D.IIIa engine, capable of 185hp.
These aircraft were preferred by the pilots, but were never available in sufficient numbers. All types of D.VII were popular with the German fighter pilots. The aircraft handled well and had light controls that made it less tiring to fly than many of its contemporaries. At medium altitude it was faster and more manoeuvrable than its opponents. It accelerated quickly in the dive while remaining steady, making it a good gun platform.
Conclusion
In its relatively brief front line career, the D.VII won itself a very impressive reputation. It was the only aircraft mentioned by name in the clause of the armistice agreement that called for the surrender of 2,000 German aircraft
Versions
V 11 : Prototype
V 21 : Prototype with tapered wings
V 22 : Prototype with four-bladed propeller
V 24 : Prototype with 179 kW (240 hp)Benz Bz IV ü engine
V 31 : One D.VII aircraft fitted with a hook to tow the V 30 glider
V 34 : D.VII development with 138 kW (185 hp) BMW IIIa engine
V 35 : Two-seat development with 138 kW (185 hp)BMW IIIa engine and undercarriage fuel tank
V 36 : D.VII development with 138 kW (185 hp) BMW IIIa engine and undercarriage fuel tank
V 38 : Prototype Fokker C1
Specifications
Crew 1
Weight Empty 700 kg Loaded 910 kg
Dimensions
Wing Area 20.20m2
Span 8.9 m
Length 6.95m
Height 2.94 m
Motorisation
Watercooled
Prototype
V.11 Mercedes D.III 160 HP
D.VII Mercedes D.IIIa 160 HP
D.VIIF BMW IIIa 185 HP
Maximum speed 190 km/hr
Ceiling 6 000 m
Endurance 350 kms
Armament 2 MG forward firing Spandau machineguns



































.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

