Luftstreitkräfte
Elle est connue sous le nom de Die Fliegertruppen des deutschen Kaiserreiches jusqu'en Octobre 116 et ensuite de Luftstreitkräfte
English Transaltion
 |
 |
 |
| 1914 1915 |
1916 - Mars 1918 |
Mars 1918 Novembre 1918 |
Voir Aussi See Also
1915 Luftstreitkräfte Major La Ferte Alais 2015
1915 Luftstreitkräfte Major La Ferte Alais 2015
1915 Luftstreitkräfte Leutnant La Ferte Alais 2015
Luftstreitkräfte Unteroffizier La ferte Alais 2015
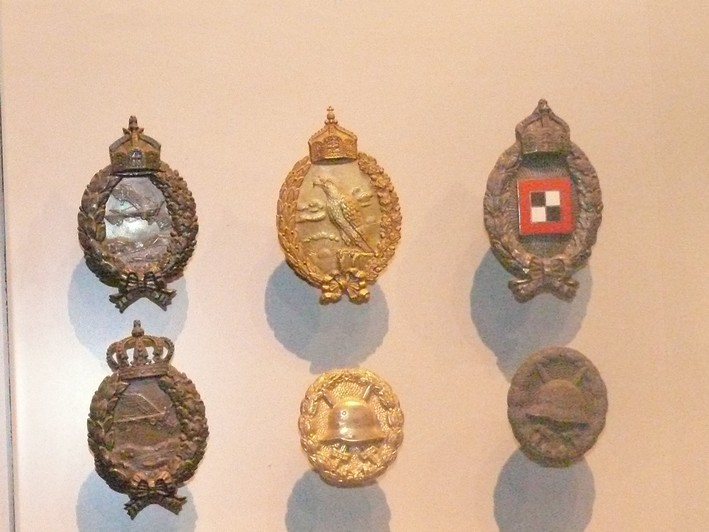
Les badges et insgines de la Luftstreitkräfte
 |
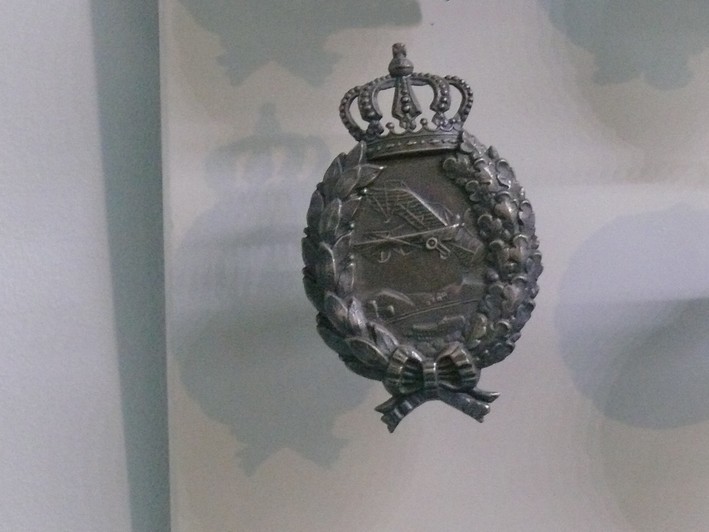 |
| Brevet Observateur prussien |
Brevet Observateur prussien Aeronavale |
 |
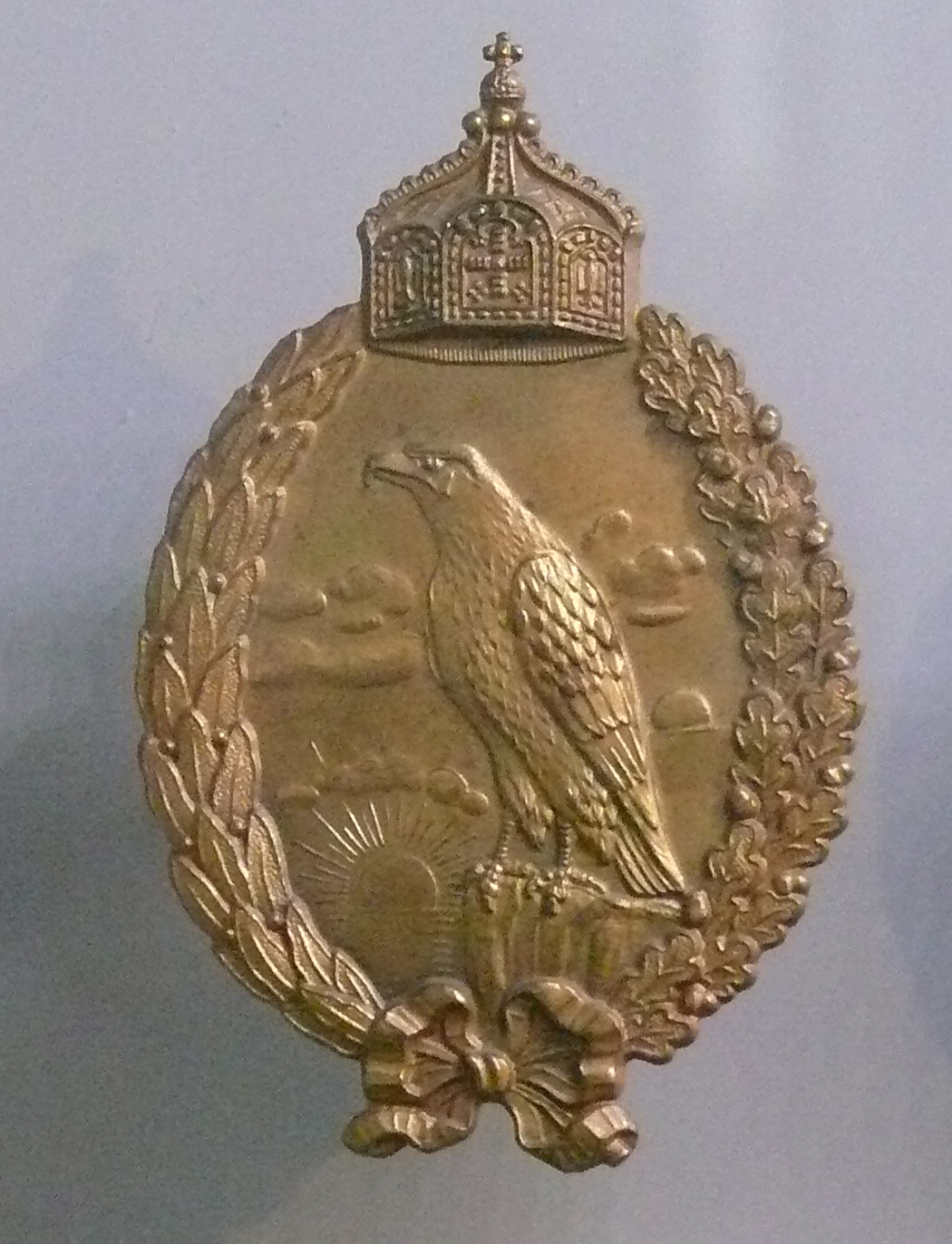 |
| Brevet PilotePrussien |
Brevet Pilote Bavarois |
 |
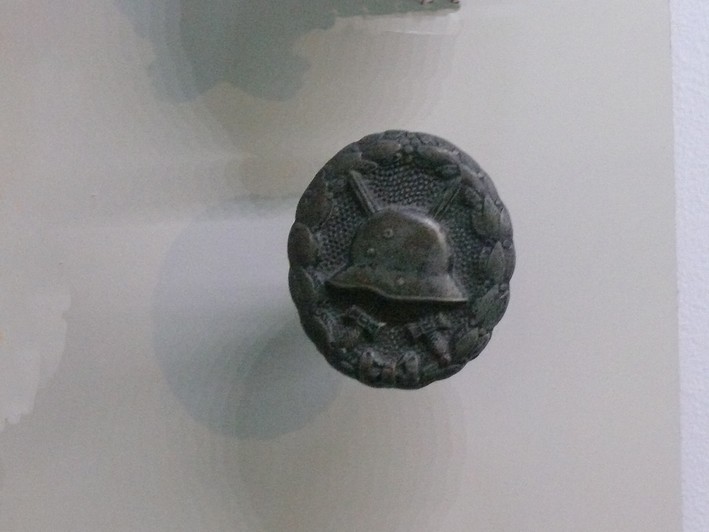 |
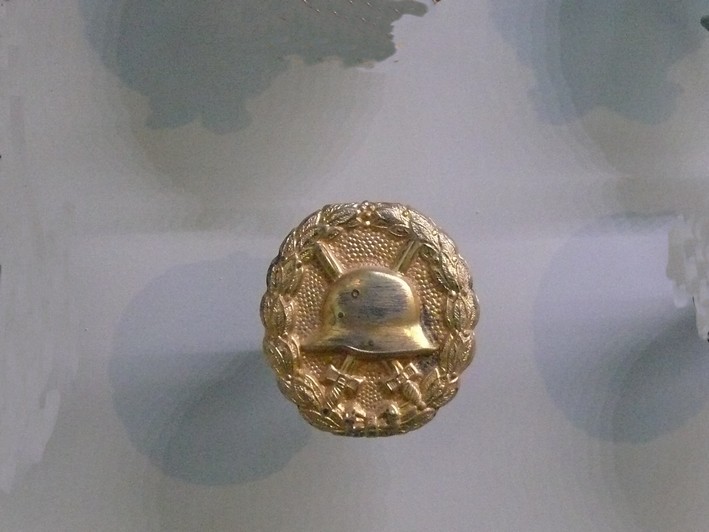
| Insigne des blessés chasse |
Insigne des blessés chasse |
|
Le système de numeration de l'Idflieg The Idflieg designation system
|
Le Idflieg( inspektion der Inspection Fliegertruppen inspection des troupes aériennes) utilise le système de désignation des avions suivant avant la fin de la 1ère Guerre Mondiale
La désignation a été simple
Nom de l'usine, suivi par lettre alphabétique suivi d'un chiffre romain
A monoplace non armés monoplan, propulsé par un moteur de moins de 150 ch (112 kW)
B biplace non armés biplan, propulsé par un moteur de moins de 150 ch
C biplace biplan armé, propulsé par un moteur de plus de 150 ch
CL légers "C" classe avion, suffisamment agile pour être utilisé comme chasseur quand il est armé.
D monoplace armé avion, propulsé par un moteur de plus de 150 ch
E monoplace armé avion, propulsé par un moteur de moins de 150 ch
F monoplace armé triplan, alimenté par un moteur de moins de 150 ch (au début seulement)
G Bombardier armé biplan avec deux ou trois moteurs (groß - la "grande"). Ces appareils étaient à l'origine désigné K (voir ci-dessous).
J biplace d’attaque au sol
K bombardier biplan armé de deux ou trois moteurs (Kampfflugzeug avions de combat). Plus tard à G (voir ci-dessus)
N nuit (nuit), bombardier biplace nocturne
R Bombardier biplan armé de quatre ou de plusieurs moteurs (Riesenflugzeug - "avion géant")
W (Wasser eau) Hydravions
Attention
Une légende tenace classe les chasseurs D comme Doppeldecker ou biplan et E comme Eindecker ou monoplan Tous les chasseurs classe D ne sont pas des biplans, idem tous les chasseur classe E ne sont pas des monoplans.
Une autre idée fausse a été nomme le Fokker triplan comme Dr (Dreidecker - "triplan") En fait le nom officiel est Fokker FI
Le système a pris fin avec la capitulation allemande de 1918
The Idflieg for Inspektion der Fliegertruppen Inspectorate of Flying Troops is the designation system used by Germany for the designations of aircrafts prior to end of WW1
The designation was simple
Name of the factory followed by Alphabetic letter followed by a Roman Numeral
A single-seat unarmed monoplane, powered by an engine of less than 150 hp (112 kW)
B two-seat unarmed biplane, powered by an engine of less than 150 hp
C two-seat armed biplane, powered by an engine of more than 150 hp
CL lightweight "C" class aircraft, nimble enough to be used as fighter when armed.
D single-seat armed aircraft, powered by an engine of more than 150 hp
E single-seat armed aircraft, powered by an engine of less than 150 hp
F single-seat armed triplane, powered by an engine of less than 150 hp (early use only)
G Bomber armed biplane with two or three engines (groß - "large"). These aircraft were originally designated K (see below).
J Ground Attack two-seat aircraft
K biplane armed bomber with two or three engines (Kampfflugzeug battle aircraft). Later changed to G (see above)
N night (Nacht) two-seat bomber
R biplane bomber armed aircraft with four or more engines (Riesenflugzeug - "giant aircraft")
W (Wasser water ) Seaplanes and flying boats (")
be carefful
A pupolar legen name fhighters D and E asDoppeldecker ("biplane") and Eindecker ("monoplane") but not all D-class aircraft were biplanes and not all E-class were monoplanes. Another misconception has been furthered by the widespread use of Dr (Dreidecker - "triplane") as an alternative to F
Thisfamous aircraft was formally known as the F.I.
The system ended with the end of German military aviation after the Armistice
Les Jastaffel
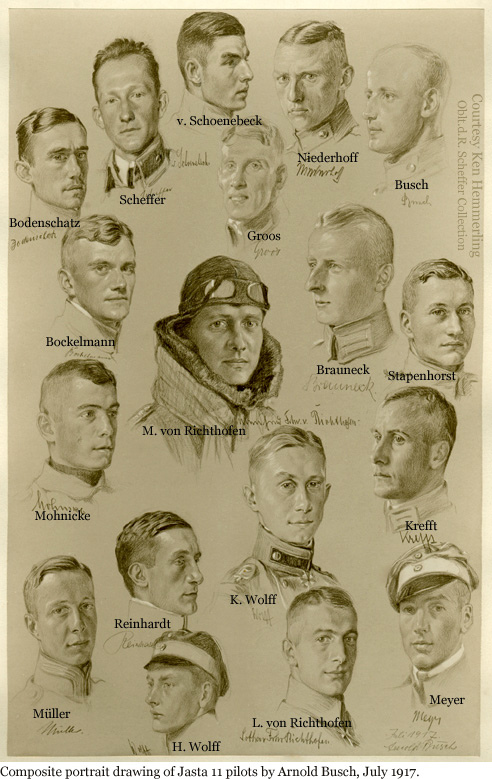 |
| Internet |
Les Avions
Voir Ce site
AEG
 |
 |
| AEG C IV |
AEG G II |
 |
|
| AEG G IV |
|
Albatros Flugzeugwerke
 |
| Abatros D XI |
AOG
 |
 |
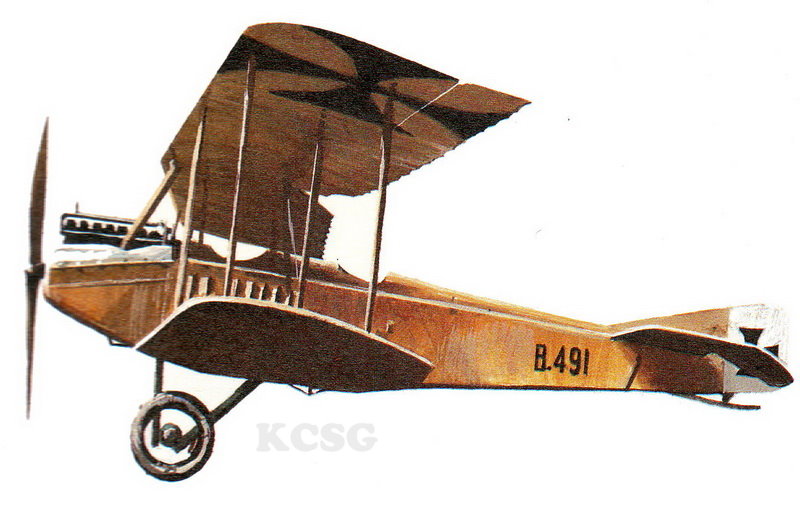
| AGO CI |
AGO CII |
 |
 |
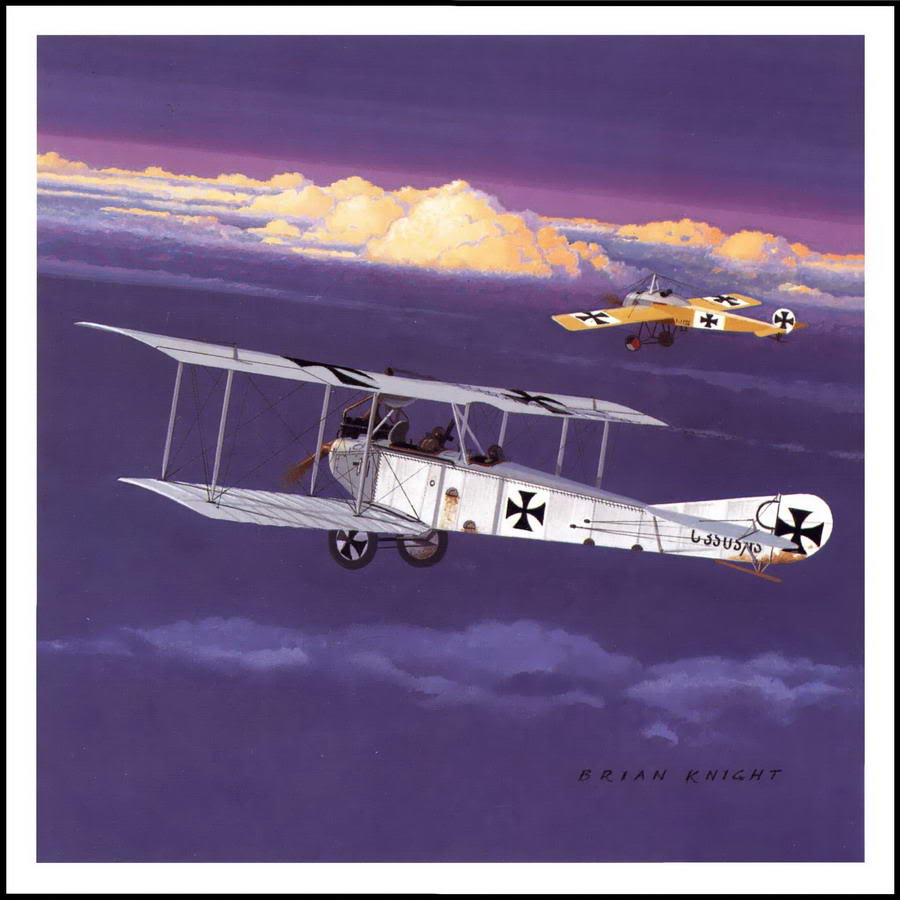
| Aviatik B I |
Aviatik B II |
 |
 |
| Aviatik B III |
Aviatik C I |
 |
 |
| Aviatik C II |
Aviatik C III |
 |
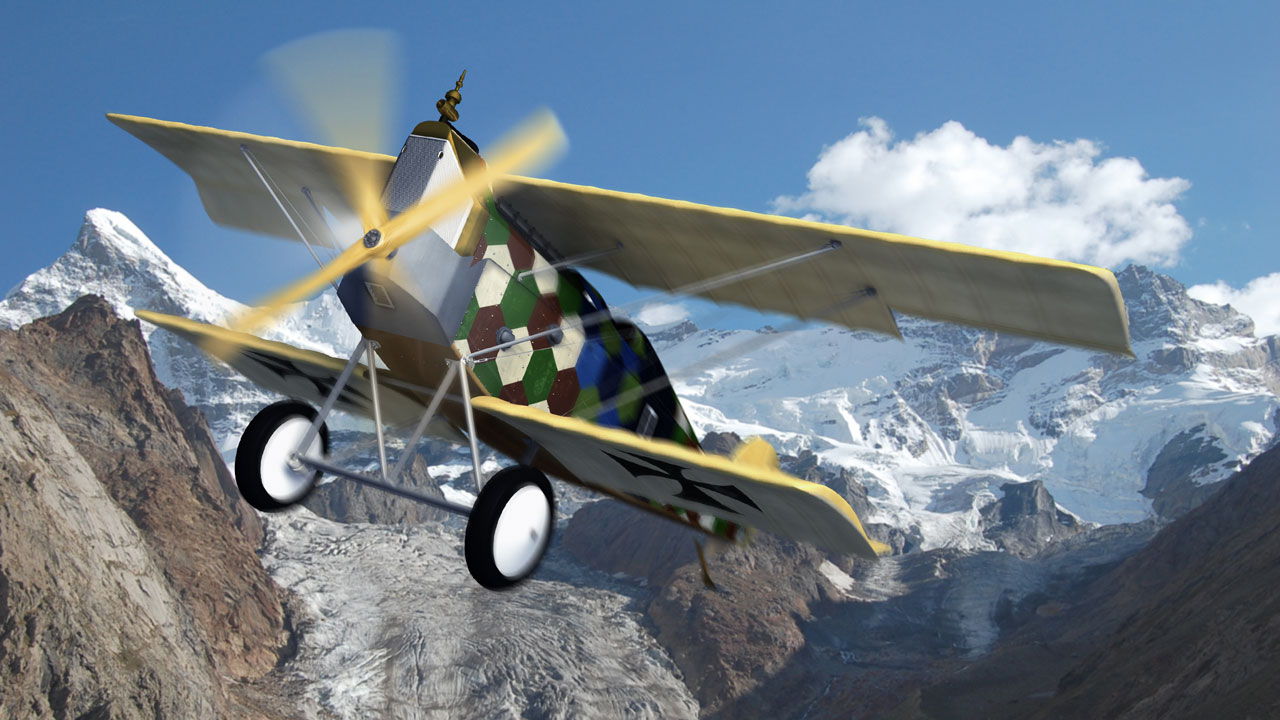 |
| Aviatik D I |
Aviatik D II |
 |
 |
| Aviatik D V |
Aviatik D VII |
Hansa Brandeburg
 |
 |
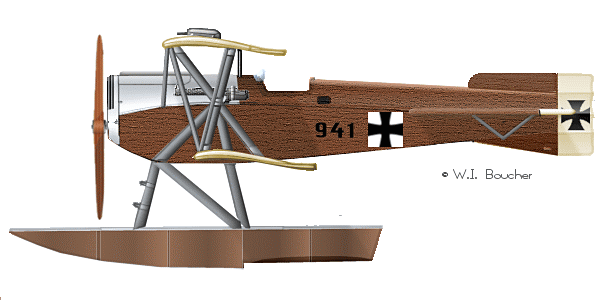
| Brandeburg B1 |
Brandeburg C 1 |
 |
 |
| Brandeburg CC |
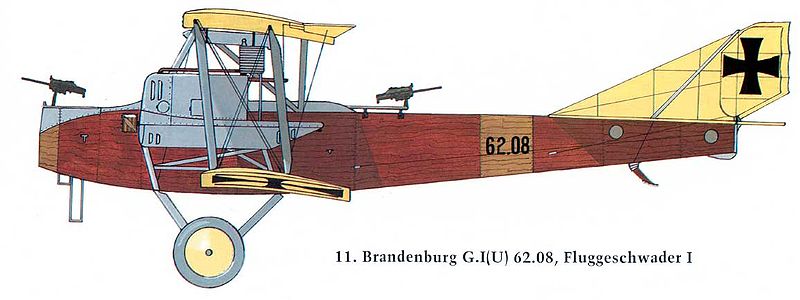
Brandeburg D I |
 |
 |
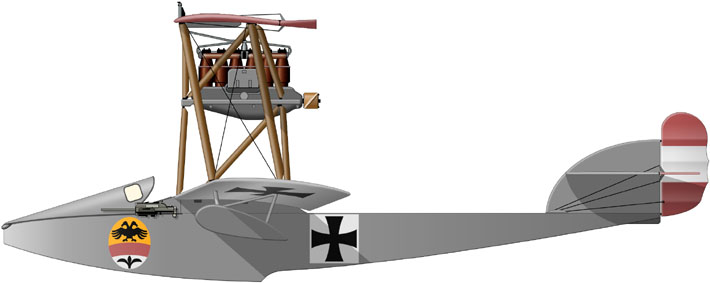
| Brandeburg G I |
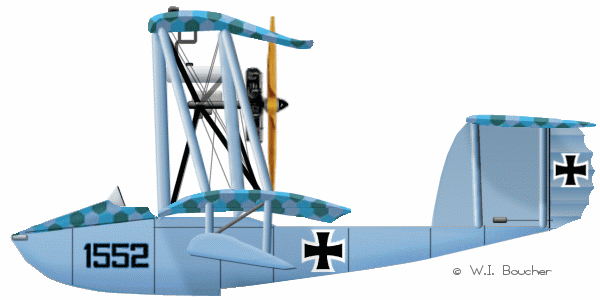
Brandeburg KDW |
 |
 |
| Brandeburg W 12 |
Brandeburg W 18-20 |
 |
 |
| Brandeburg W 33 |
Brandeburg W 29 |
Deutsche Flugzeug-Werke
 |
 |
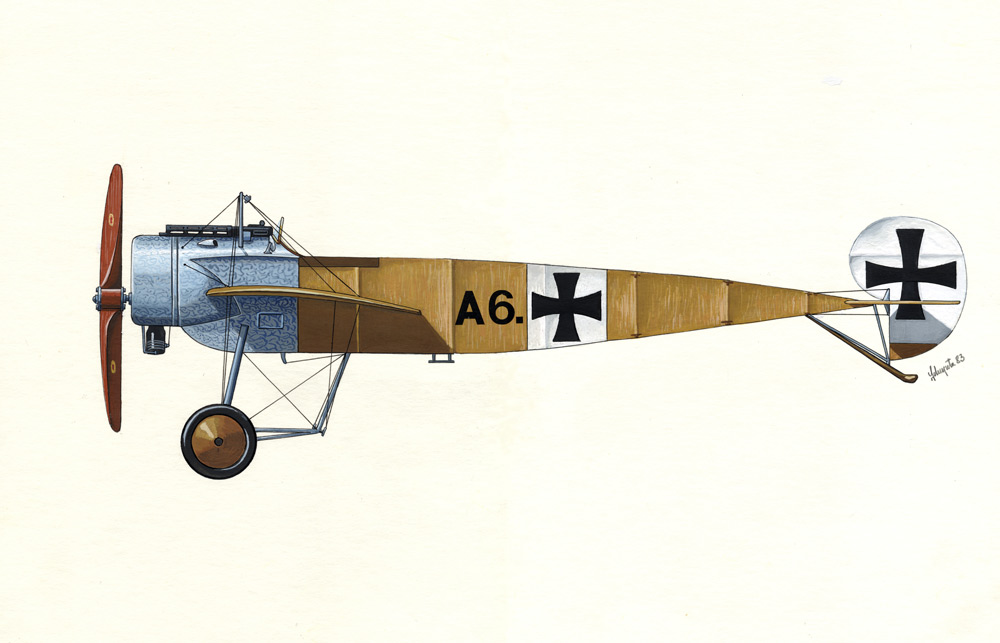
| DFW C V |
DFW C V |
 |
 |
| Fokker B III |
Fokker D II |
 |
 |
| Fokker D VI |
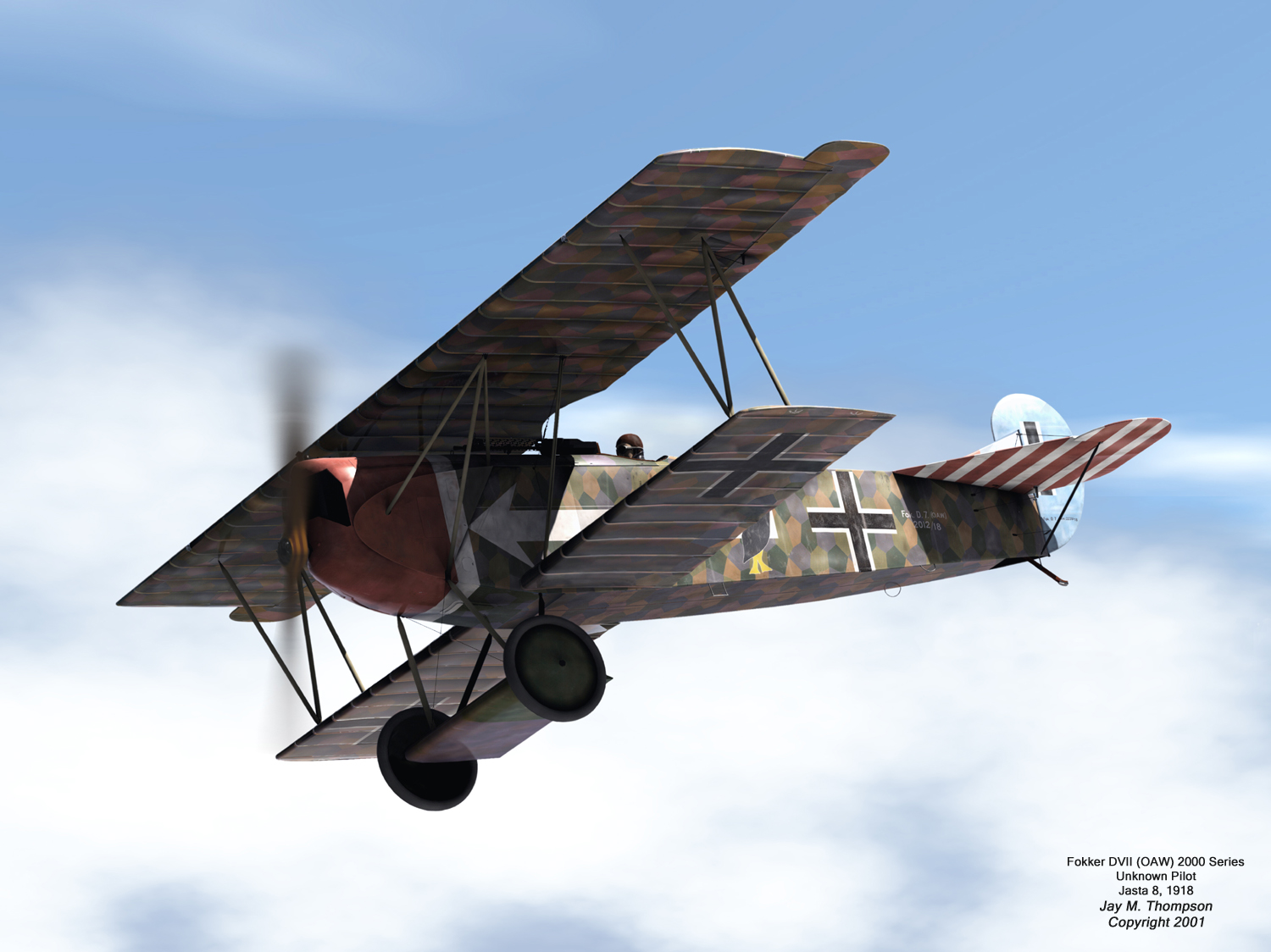
Fokker d VII Jasta 8 |
 |
 |
| Fokker D VIII |
Fokker E IV |
 |
|
| Fokker Dr I |
|
Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen
 |
| Friedrichshafen GIII |
Gothaer Waggonfabrik
 |
 |
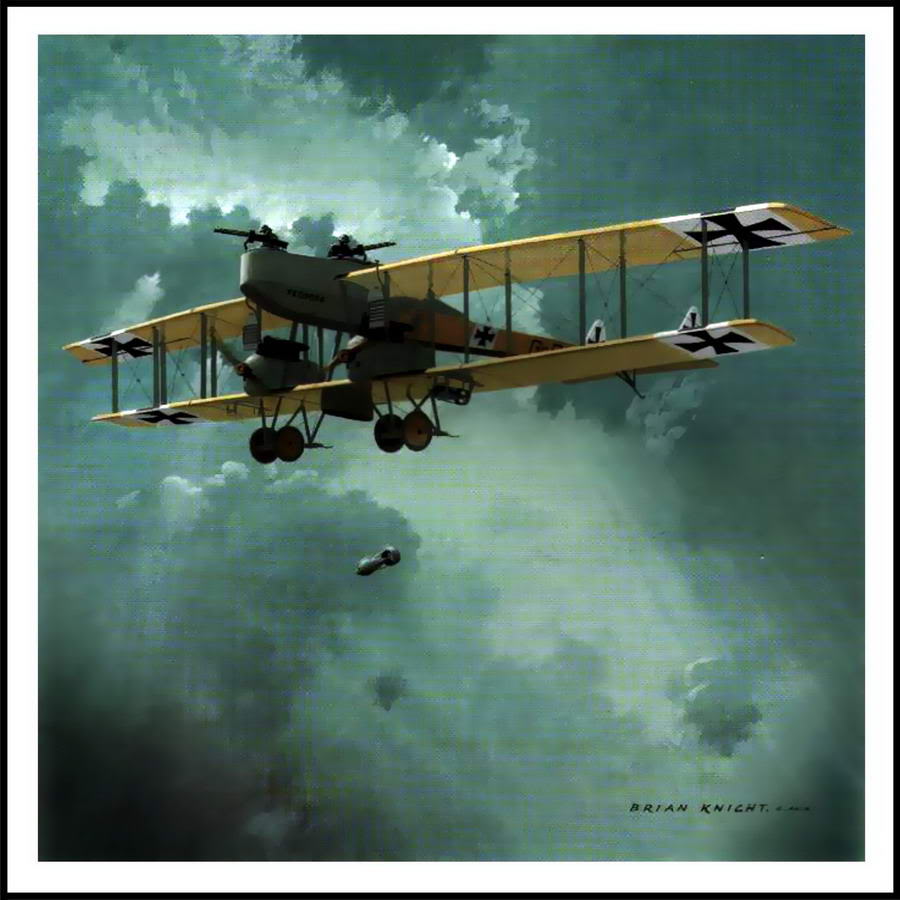
| Gotha G 1 |
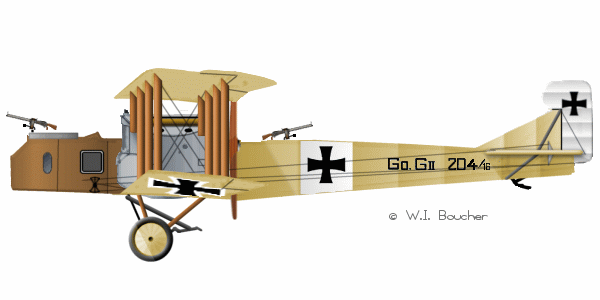
Gotha G II |
 |
 |
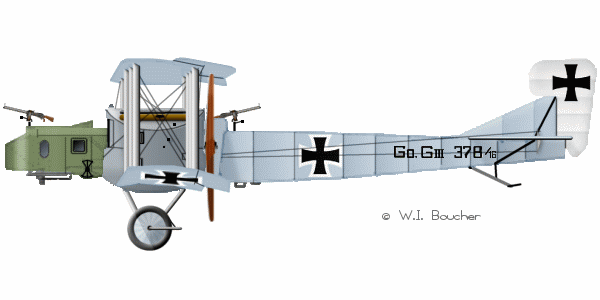
| Gotha G III |
Gotha G IV |
 |
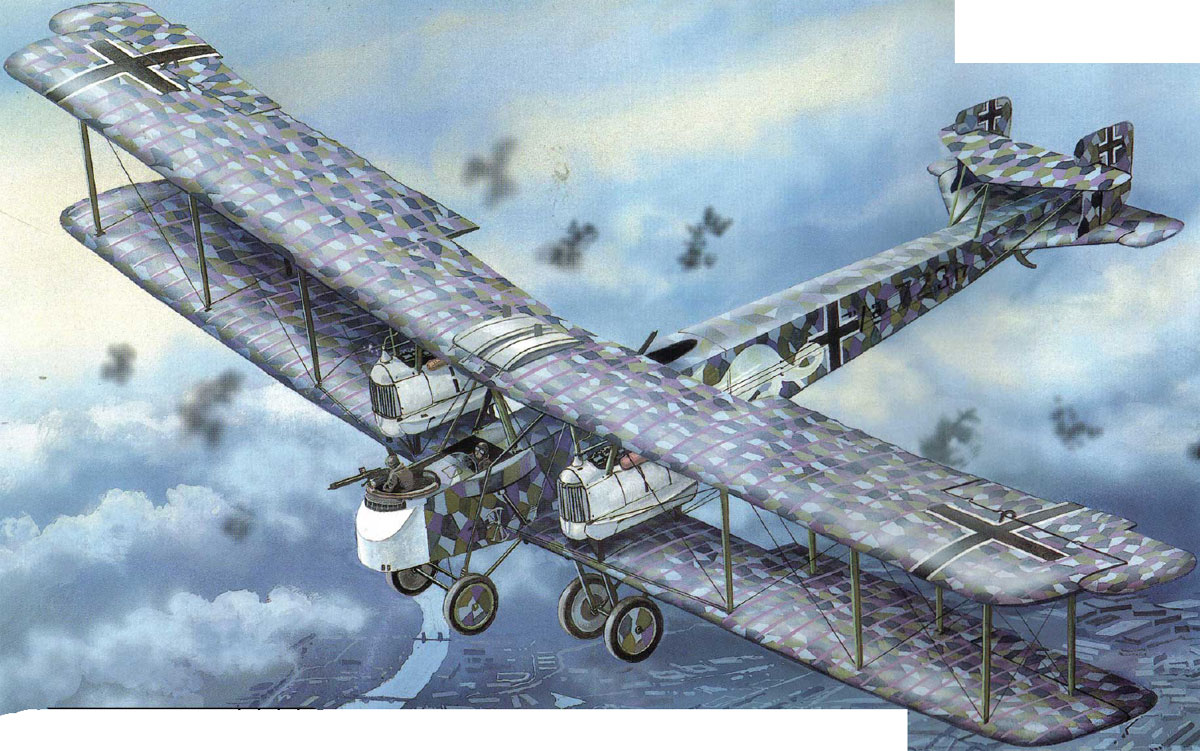 |
| Gotha G V |
Gotha G V a |
Halberstadt
 |
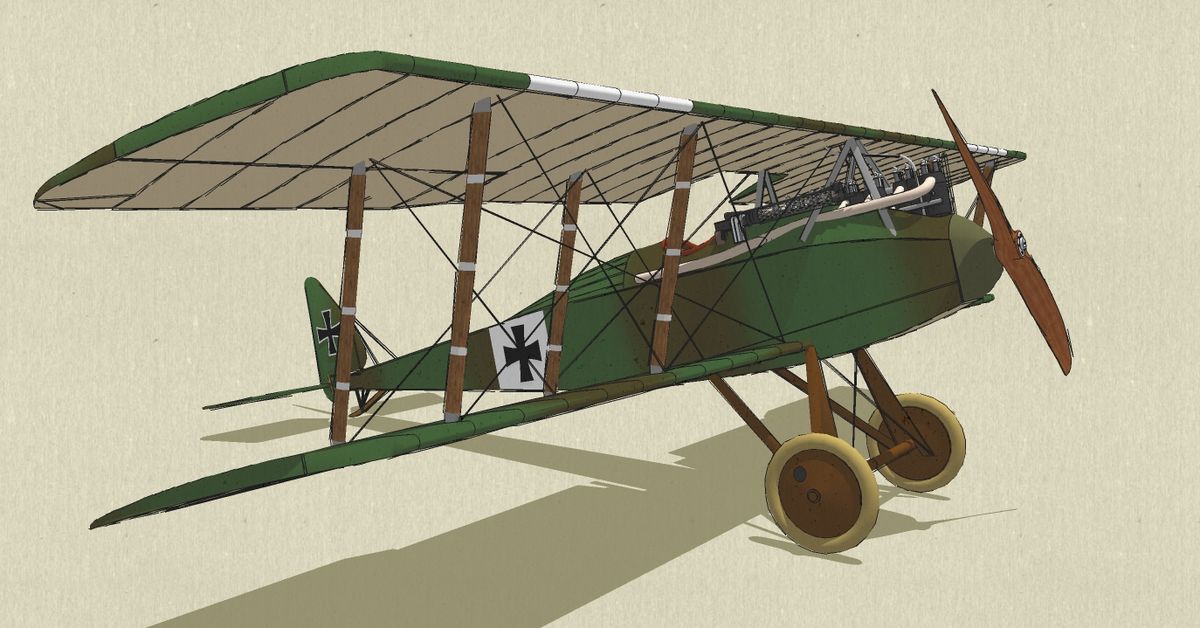 |
| Halberstadt CL II |
Halberstadt D II |
 |
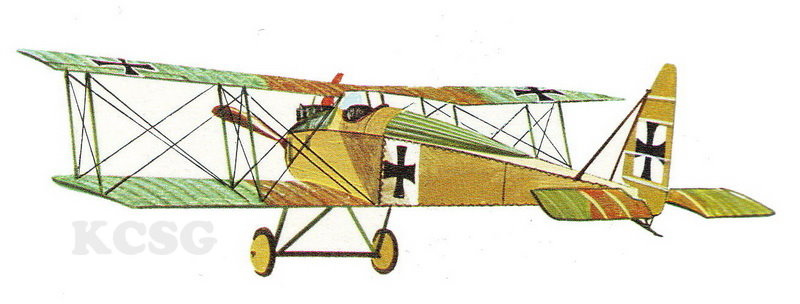 |
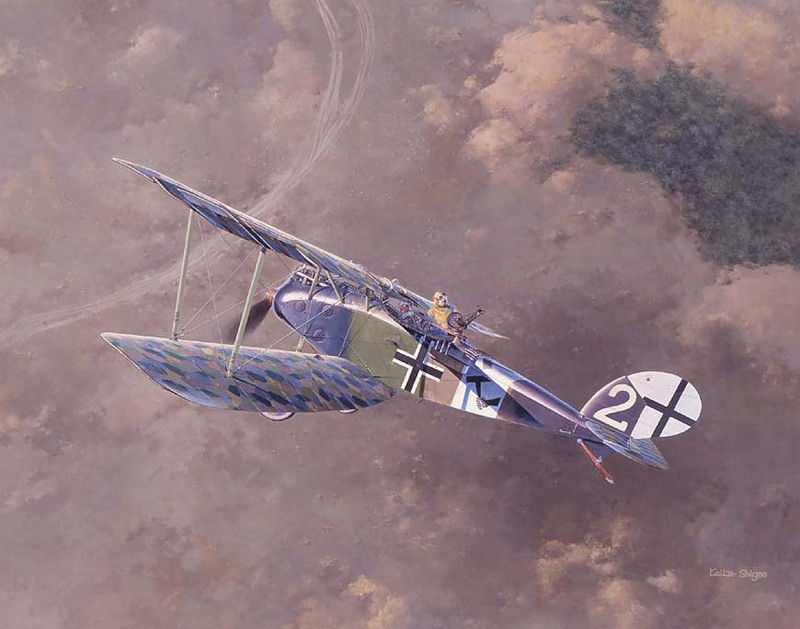
| Halberstadt CL IV |
Halberstadt D II |
Hannover
 |
 |
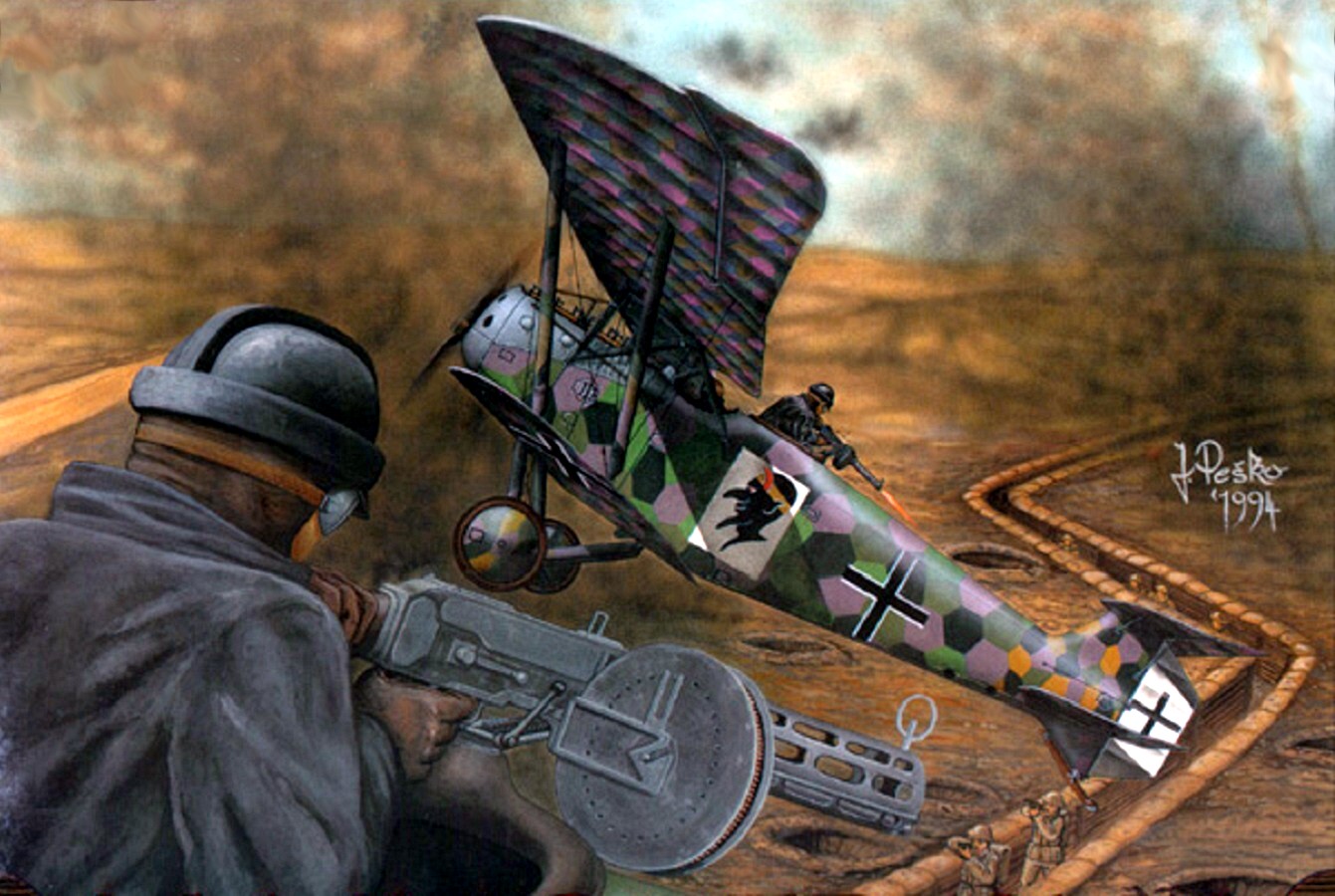
| Hannover CL III |
Hannover CL III |
Junker
 |
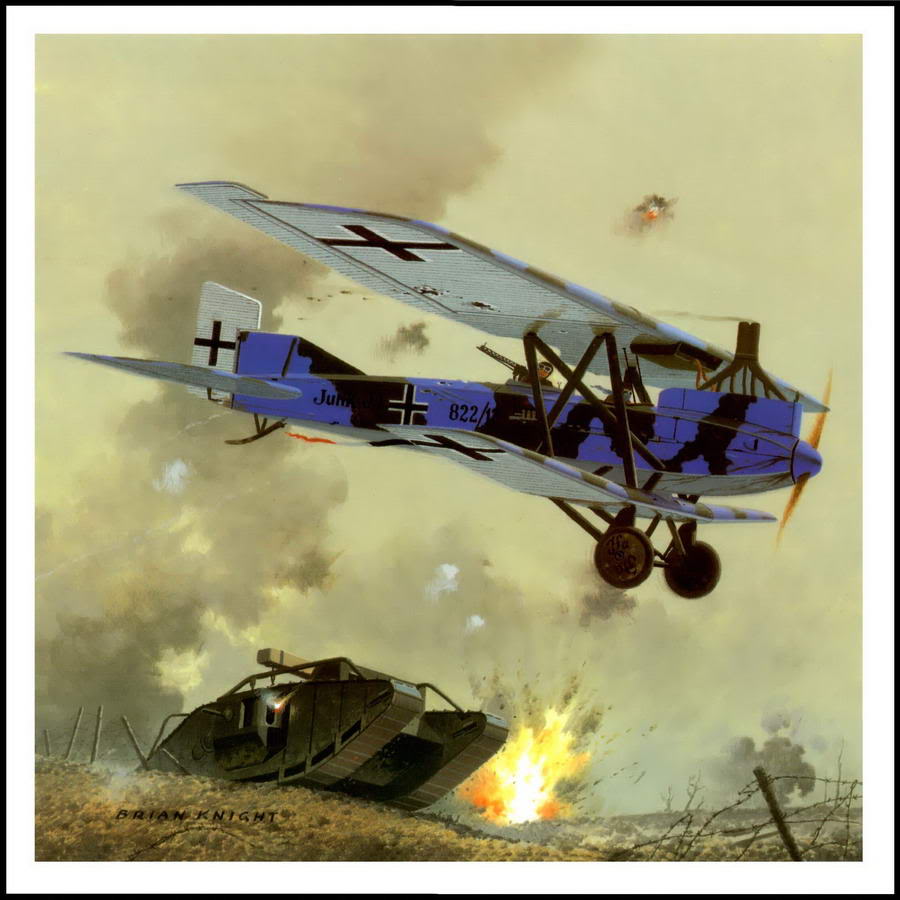 |
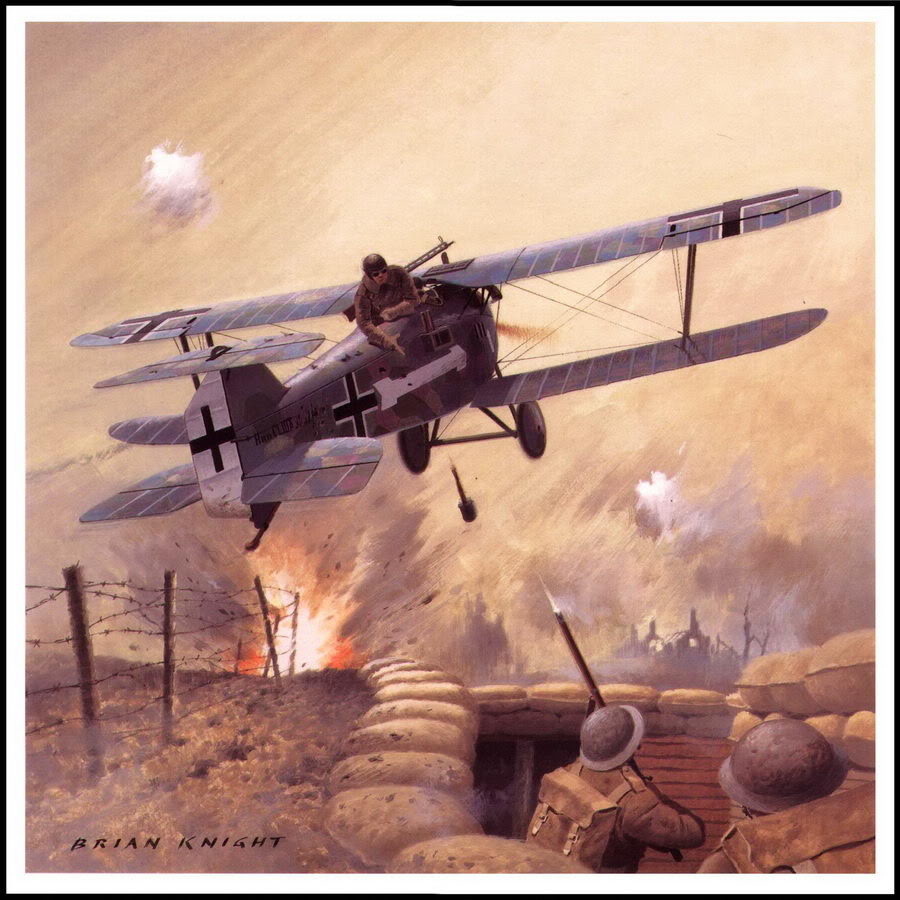
| Junker D I |
Junker J I |
Linke Hoffmann
 |
| Linke Hoffmann R II |
LFG Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft (Roland)
 |
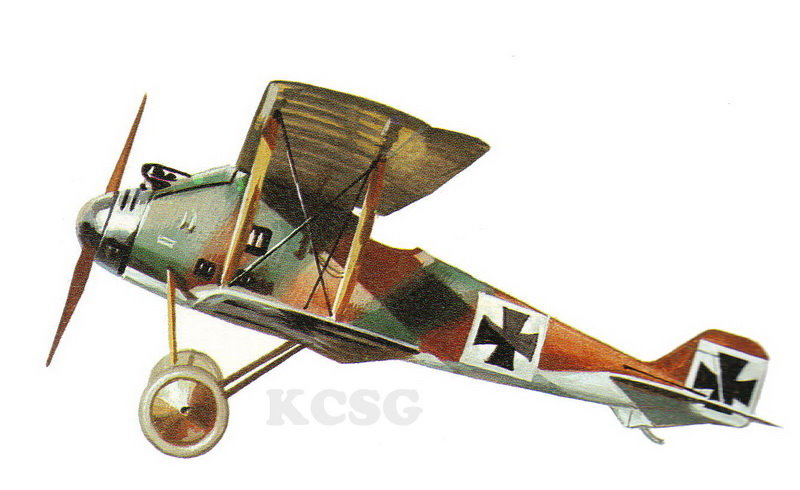 |
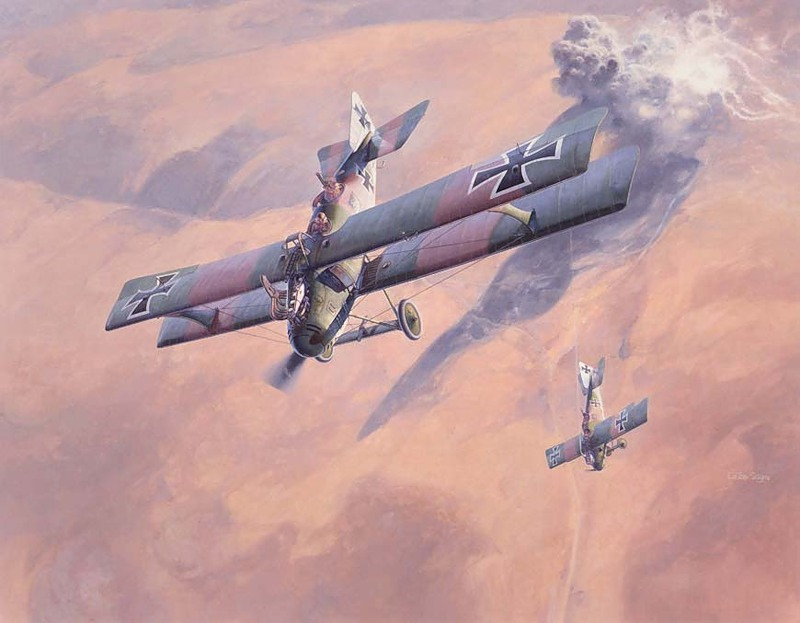
| Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft CII a |
Luft-Fahrzeug-GesellschaftD II |
 |
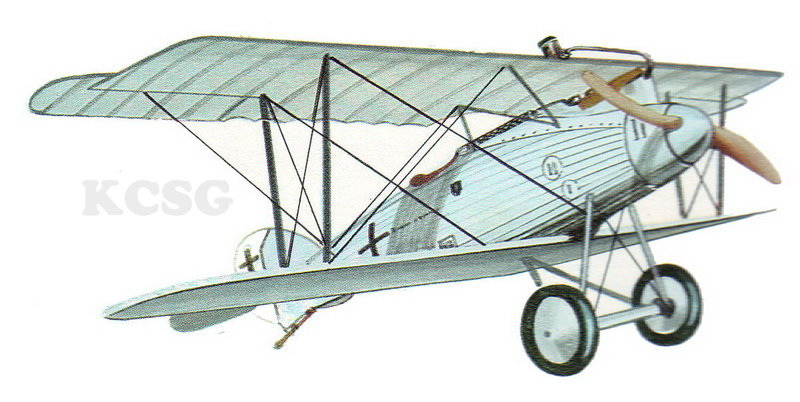 |
| Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft D VI |
Luft-Fahrzeug-Gesellschaft DVI b |
LVG
 |
 |
|
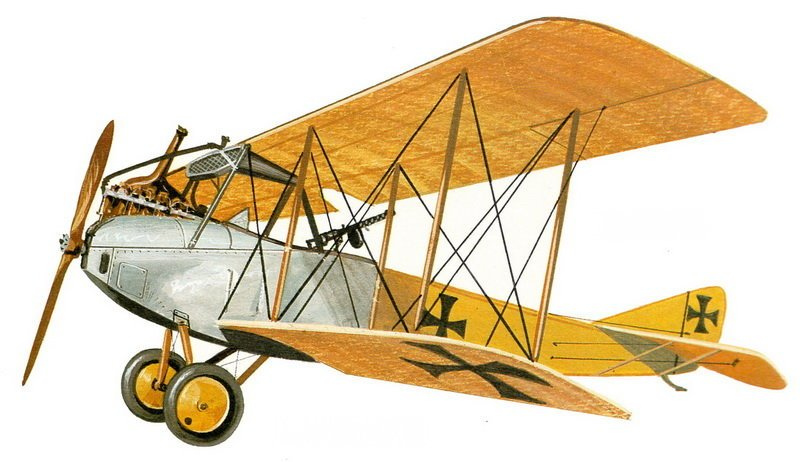
LVG B I
|
LVG C II
|
 |
 |
| LVG C V |
LVG C VI |
Mannesmann
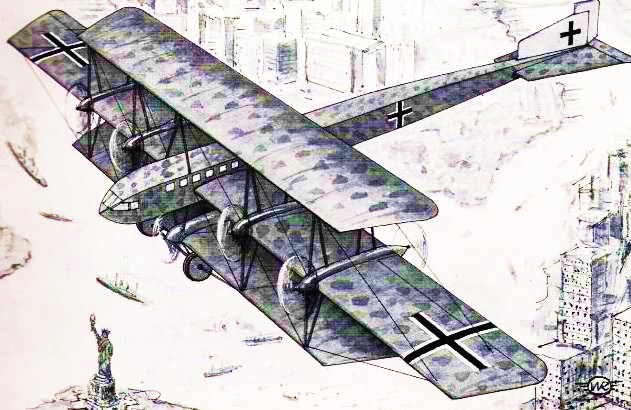 |
| Mannesmann-Po |
Pfalz
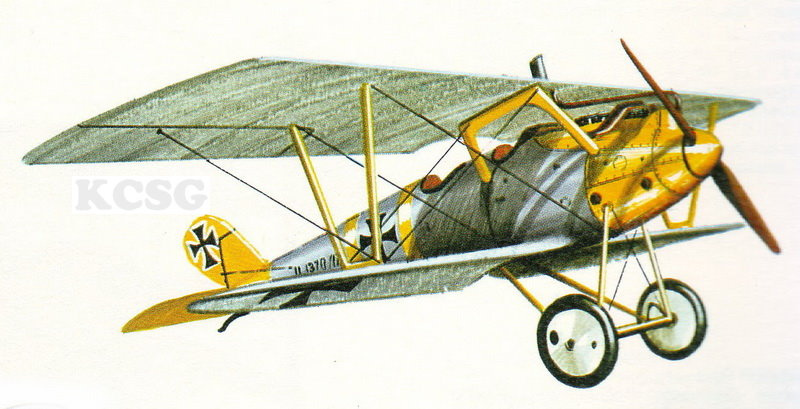 |
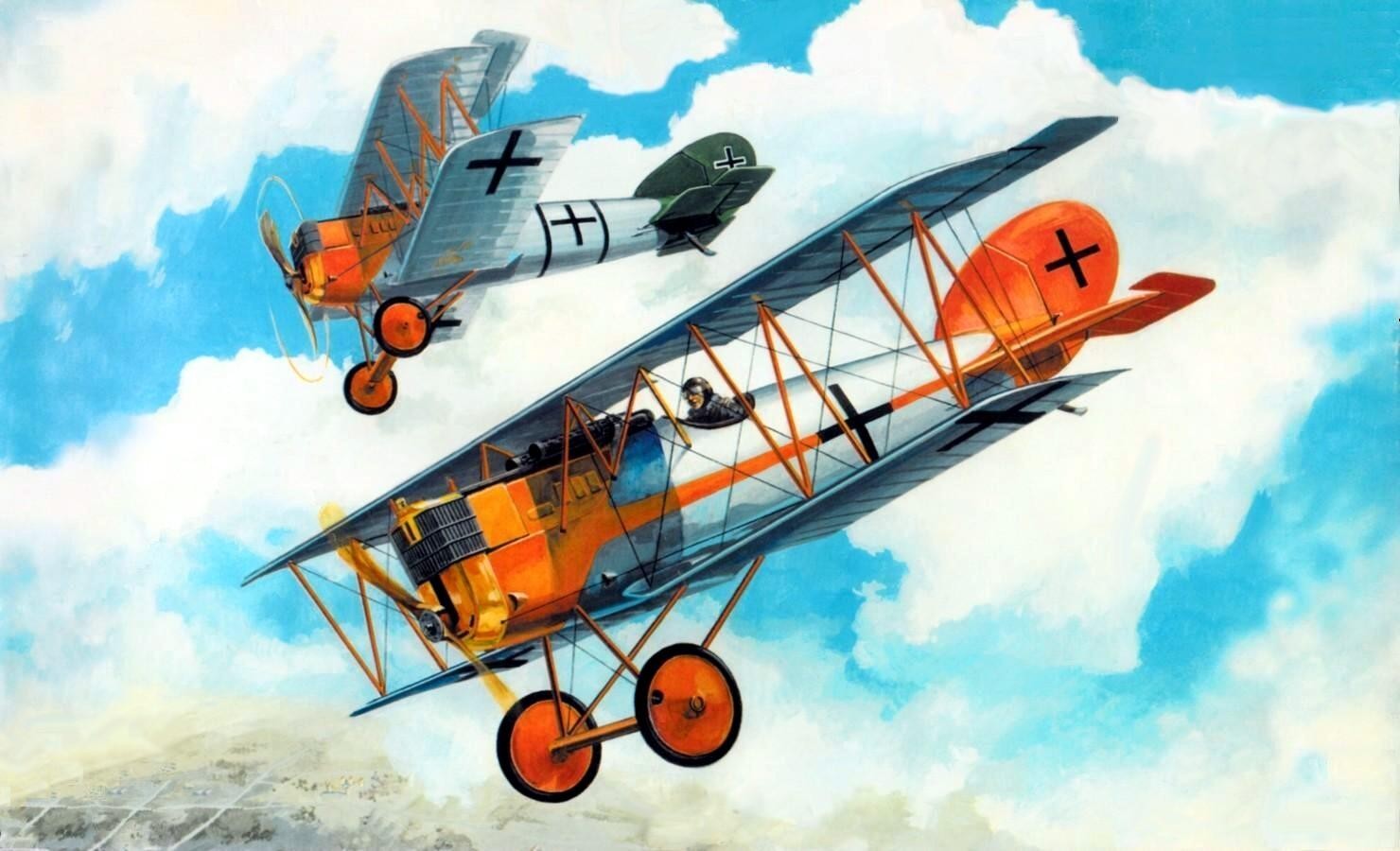 |
| Pfalz D III |
Pfalz DXII |
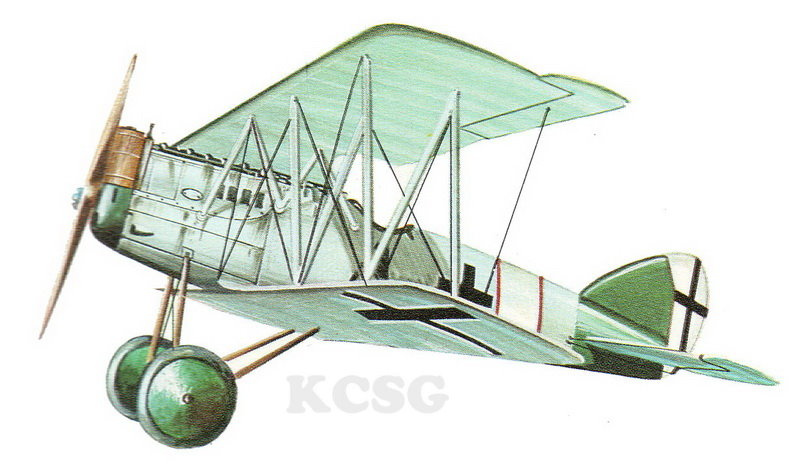 |
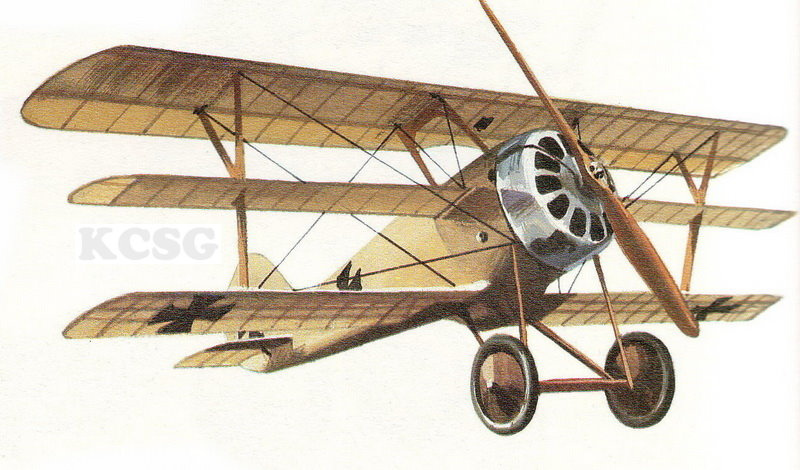 |
| Pfalz DXII |
Pfalz D r I |
Phonix
 |
 |
|
Phonix C1
|
Phonix D1
|
Rumpler
 |
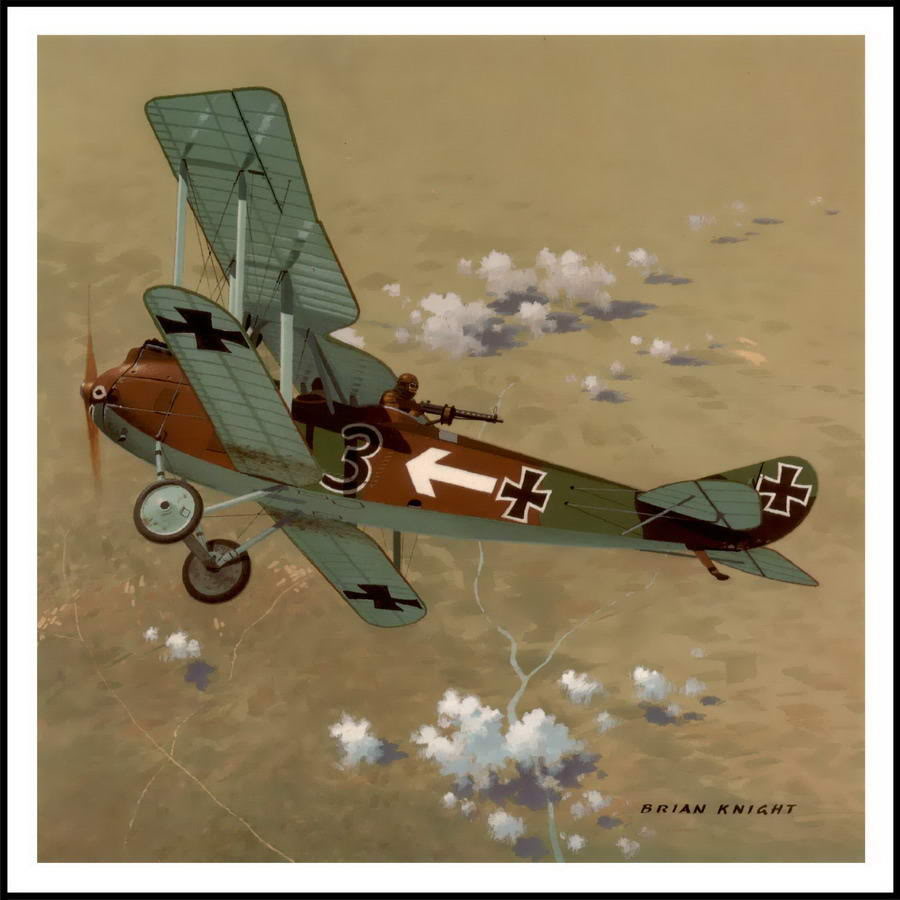 |
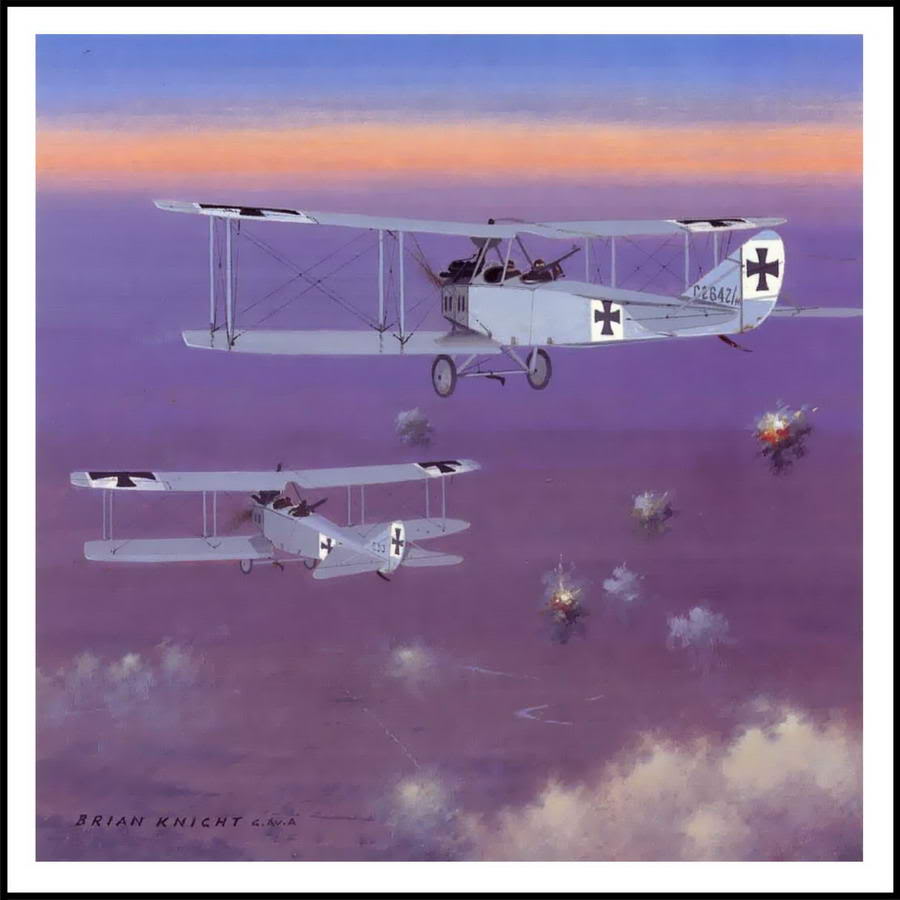
| Rumpleer C 1 |
Rumpler C IV |
 |
| Rumpler VI B 1 |
Siemens Schuckert
 |
 |
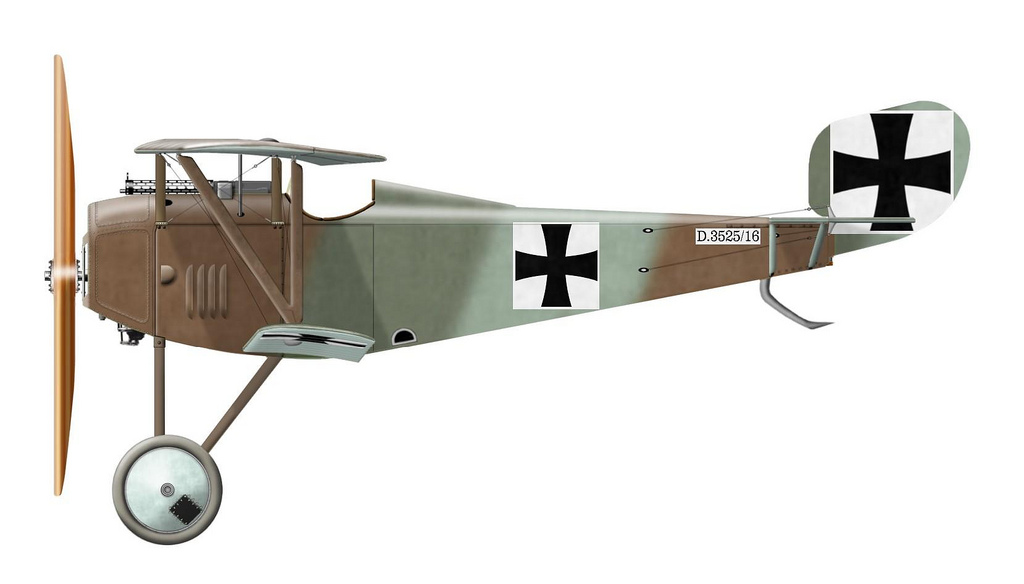
| Siemens Schuckert D I |
Siemens Schuckert D III |
UFAG
 |
|
UFAG cI
|
Zepellin
 |
| Zepellin Staaken R VI |