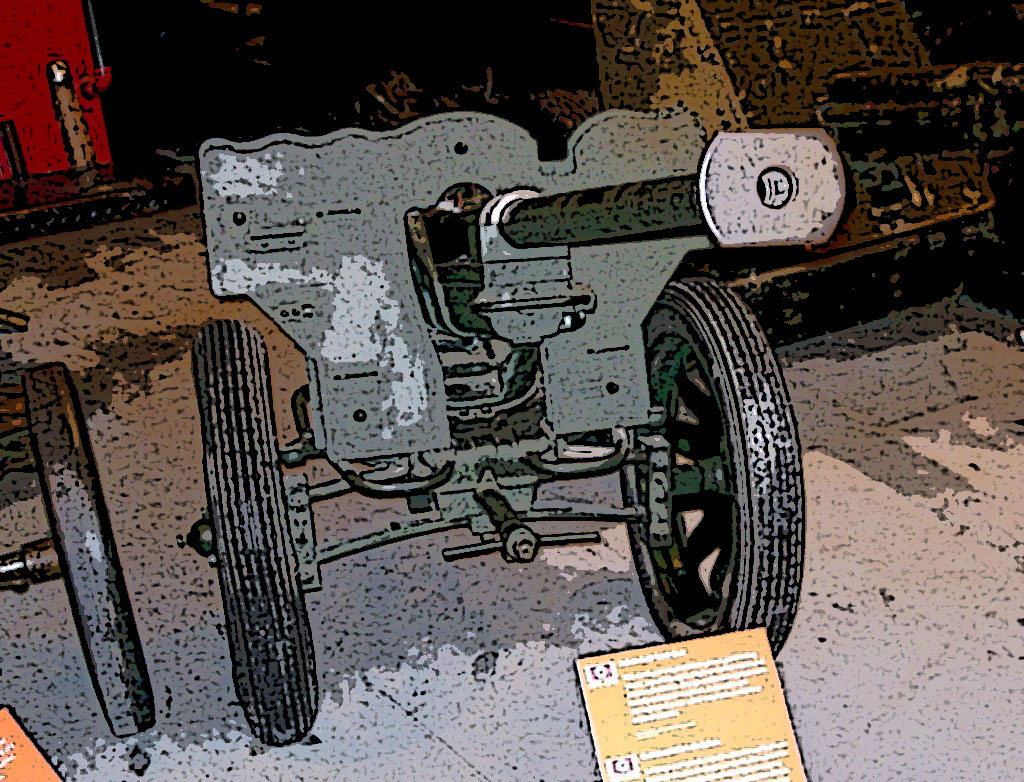
2.8 cm sPzB 41 Saumur
English Transalation
tiré de cet article
2,8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41
Le 2,8 cm sPzB 41 est une arme anti char à âme conique En anglais ce type d’arme produit un mouvement appelé squeeze bore" principle
Cette arme a été officiellement classé comme un fusil anti-char lourd (schwere Panzerbüchse), même si bon nombre des caractéristiques la classe comme un canon anti-char léger
Description
Bien qu'il ait été sPzB- ou fusil anti-char lourd (schwere Panzerbüchse) c’est un canon léger antichar L'arme a un mécanisme absorbant le recul et elle possède un affut sur roues avec bouclier de protection Le seul élément important de cette arme qui soit similaire à celui des fusils anti-char, est la présence d’un système de visée rudimentaire.
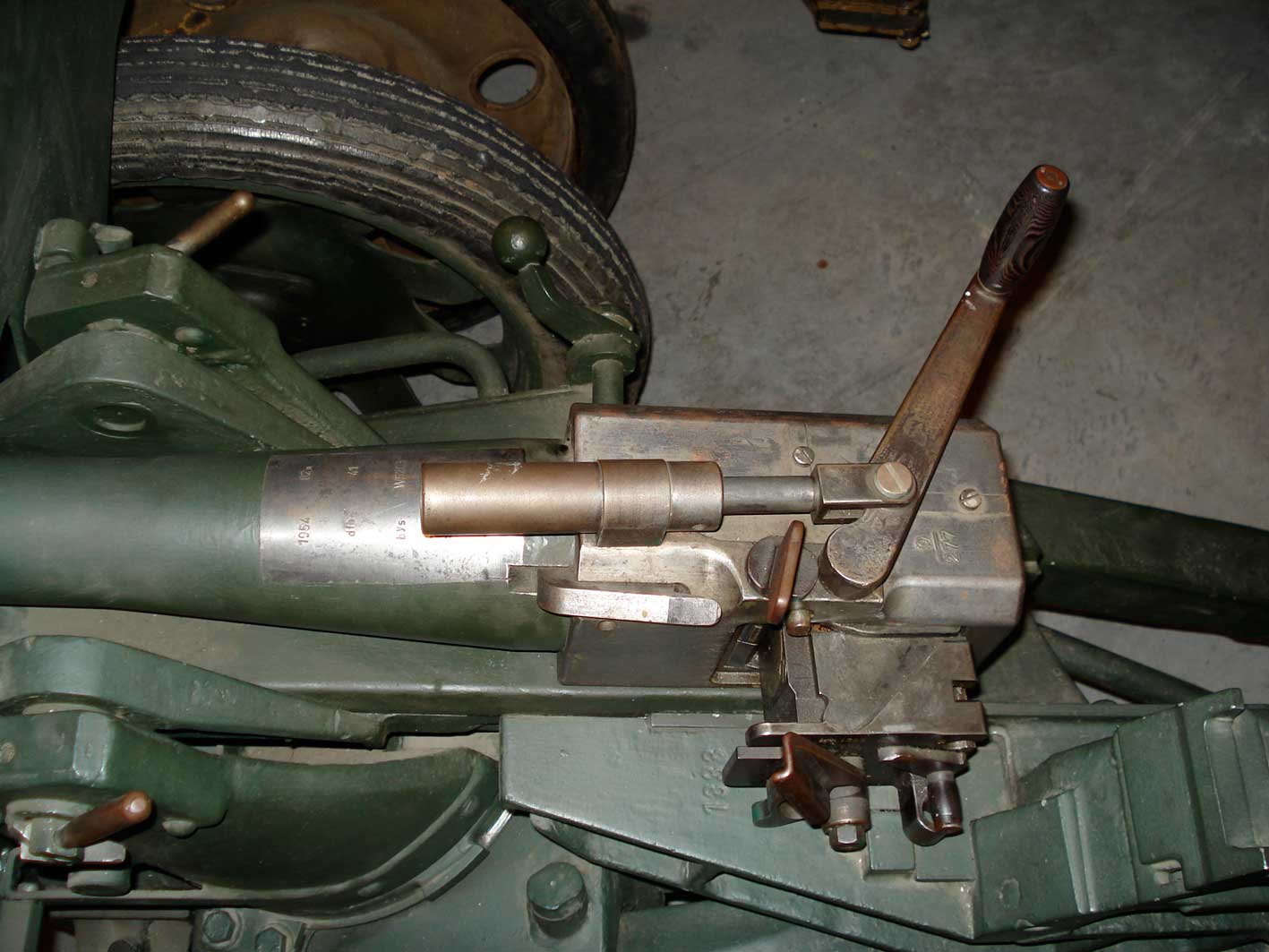 |
| Culasse ( Wikipedia) |
Le point le plus important de cette âme est l’âme conique du canon qui se réduit de 28 millimètres (culasse) à 20 mm au frein de bouche
Ce qui donne une grande vitesse au projectile qui atteint 1400m/s . Ceci est permit par l emploi d’une bague en métal qui entraine l’alésage du projectile
Il possède aussi un frein de bouche
Elle est équipée d’un système de visée portant à 500m. et la lunette de visée du 3.7cm 35/36 Pak peut y être montée.
L'arme est munie d'un dispositif de recul hydraulique amortissant le choc
Le châssis a un train de roulement avec pneumatique monté sur ressort Il peut aussi en hiver être équipé de ski
Les roues peuvent être enlevées, réduisant ainsi la silhouette globale du canon et facilitant ainsi le camouflage
Cette opération ne dure pas plus de 30/40 secondes pour un équipage entrainé
L’arme aussi peut être démontée en 5 fardeaux dont le plus lourd pèse 62 kg, ce qui permettrait un transport facile et un emploi par les troupes parachutistes.
Développement et production
Le brevet pour le projectile utilisant ce concept date de 1903 .Il est l’œuvre de l’ingénieur allemand Karl Puff.
Dans l'entre-deux guerres, un autre ingénieur allemand Gerlich continue les travaux et on fabrique un fusil anti-char fusil expérimental de 7 mm avec une vitesse (V°) de 1800 m / s
Sur ces bases en 1939-1940 Mauser-Werke AG, Oberndorf am developpe une nouvelle arme antichar de 28/20 mm initialement désigné comme 231 ou MK.8202 Gerät.
À l'été 1940 a été une série de 94 unités est envoyée en corps de troupe pour test (selon certaines sources, seuls 30 armes seront envoyées )
Après diverse modifications en 1941 est ms en fabrication le 2,8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41 de série.
Son prix de 4520 RM doit être comparé au prix d’un 5 cm Pak 38 qui coute environ 10600 RM.
La production a continué jusqu'en 1943,mais la pénurie de tungstène, entraine la cessation de la fabrication de munitions
Le 2,8 cm sPzB 41 fut une arme tres fiable
Organisation et structure
 |
 |
| Internet |
Internet |
le 2,8 cm sPzB 41 a été utilisé par certaines divisions motorisées, des unités d'infanterie mécanisée, de montagne et parachutiste.
Plusieurs armes ont également dotées les unités anti-char et des unités du génie.
L'arme a été déployée depuis le début de l’opération Barbarossa , mais aussi en Afrique du Nord, en Sicile et sur le Front de l'Ouest en 1944-1945.
À courte distance le 2.8 cm sPzB 41 c’est une arme mortelle pour les chars legers et moyens .Des rapports font état de destruction de KV 1 et JS 2
Versions
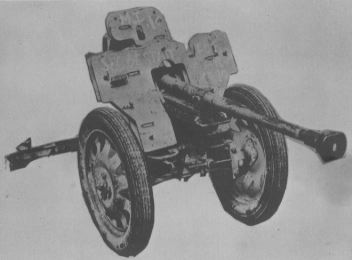 |
| 2,8 cm sPzB 41 Version de base, |
2,8 cm sPzB 41 Version de base,
Année d'origine - 1940 production - 1940 à 1943 En service 1941 à 1945
Fabriquant Mauser Werke AG, Oberndorf am Neckar
Production 2797
Caliber - 28/20 mm
Poids - 229 kg
Equipage 3
Longueur - 2,690 mm
Longueur du canon - 1.730 mm
Largeur - 965 mm
Hauteur - 838 mm
Site -5 ° à 30 °
Azimut - 70 °
Cadence de tir - 30 coups par minute
Vitesse initiale ( V°)- 1.400 m / s
Porteé 500 m
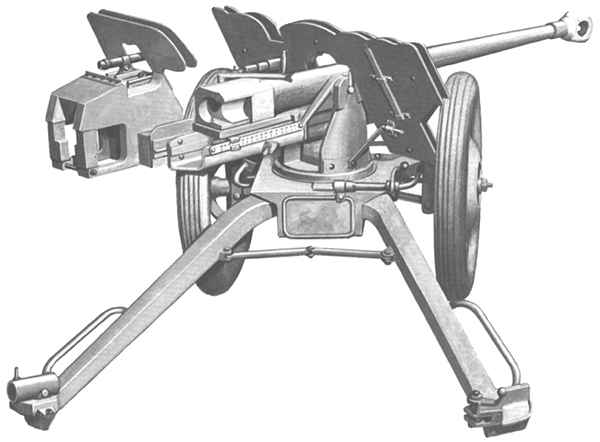
2,8 cm sPzB 41 leFl 41 (2,8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41 auf leichterfeldlafette 41)
 |
| 2,8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41 auf leichterfeldlafette 41 |
Version développée pour les unités aéroportées.
châssis léger et sans suspension, avec roues plus petites
Poids 139 kg (118 kg sans le système de transport
Châssis put pivoter sur 360 ° et en azimut de -15 ° à 25 °
2,8 cm KwK 42
Modification de 24 pièces On ne sait pas si elles furent utilisés en dehors des essais.
Le sPzb 41 est monté sur le SdKfz 250/11,et aussi sur des SdKfz 221
Munitions
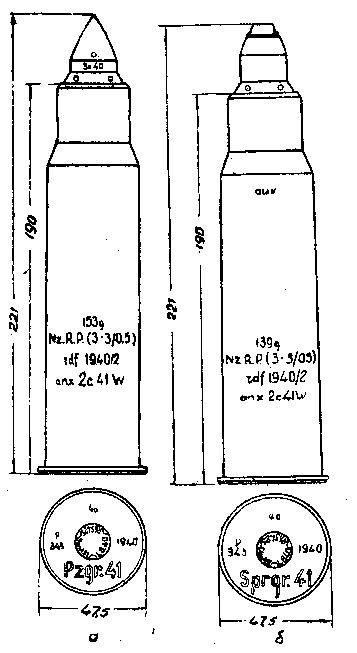 |
| Munitions (Internet) |
Il existe deux types de munitions conçues pour sPzB 2,8 cm
- 2,8 cm perforante Pzgr.41 production de munitions512 600 pcs
- 2,8 cm cluster Sprg.41 avec cartouche de 5 g de PETN (tétranitrate de pentaérythritol, ou penthrite) production de munitions 1 602 800 pcs
Production de 2,8 cm sPzB 41
1940 94 pc
1941 349 pcs
1942 1030 pcs
1943 1324 pcs
Total 2797 pcs
Penetration 2,8 PzGr. 41
100m/60 ° / 52 (69 mm)
100m/90 ° / 75 mm
300m/60 ° / 46 mm
400m/90 ° / 40 mm
500m/60 ° / 40 (52 mm)
2.8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41
from this article
2.8 cm sPzB 41 German anti-tank weapon was working on a tapering (conical) mainly. In British English literature written word is used "The squeeze bore" principle. The weapon was officially classified as a heavy anti-tank rifle (schwere Panzerbüchse) even though many of the characteristics of her rank as a light anti-tank guns.
Description
Although it was sPzB-41 is classified as a heavy anti-tank rifle (schwere Panzerbüchse), in favor of the easy categorization of anti-gun say the following facts. The weapon should be a mechanism to control rear-nature.
The weapon also had the chassis (wheeled or skids) and cover to protect the operator. The only significant element in common with anti-tank guns was the absence of a mechanism to control and measure measured weapons. With a relatively light structure was measured and measured manually operated weapons.
 |
| Breech ( Wikipedia) |
The most interesting element of the weapon was its conical bore the reduced caliber of 28 millimeters from the breech (inclusive) to 20 mm at the mouth mainly. Project was vybanený two rings of soft metal, which is the way distort the bore. The result of this construction was ús?ová high speed projectile firing, and 1400 m / s! At the end was especially fitted ús?ová brake. Horizontal end chamber is blocked automatically when charged. The weapon was fitted with open sights to a distance of 500m. Telescopic sight of 3.7cm Pak 35/36 could also be fitted.
The weapon is fitted with hydraulic-mechanical damping device back nature. The chassis has been variableHe has rubber tires or rubber wheels mounted through the suspension of the support frame. There was also variation in winter traverse skids.
Wheels can be removed, thus reducing the overall silhouette of the machine facilitates the disguise.
The whole operation did not last the crew trained more than 30-40 seconds.
Concept weapons permit its distribution into five pieces, the most difficult and weighed 62 kilograms, which would allow transport without the use of technology and done a good weapon, inter alia, the paratrooper.
Development and production
Technique used mainly tapering and distorting the projectile first patented in Germany in 1903, designer Karl Puff. In the interwar period, continued to develop another German engineer Gerlich. The result of his efforts was 7 mm with an experimental anti-tank rifle ús?ovou speed 1800 m / s!
On these bases began in 1939-1940 armory Mauser-Werke AG, Oberndorf am Neckar with the development of entirely new 28/20 mm anti-tank weapon was originally designated as 231 or MK.8202 Gera. In the summer of 1940 was a series of 94 guinea units (according to some sources, only 30) passed Army testing.
After the small adjustments in 1941 launched under the designation 2.8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41-series. Production price for each piece was estimated at RM 4520.To compare the cost price 5 cm Pak 38 is at about RM 10,600.
Production continued until 1943, when it was the lack of tungsten, needed to manufacture ammunition stopped.
Despite serving 2.8 cm sPzB 41 reliably throughout the rest of the war.
Organization and structure
 |
 |
| internet |
internet |
2.8 cm sPzB 41 had been used by some motorized divisions, mechanized infantry units, mountain and paratrooper. Several pieces were also delivered anti-tank and engineer units. The weapon has been deployed since the beginning of eastern crusade, but appeared also in North Africa, Sicily and Tallinn and the Western Front in 1944-1945.
At a short distance to 2.8 cm sPzB 41 excluded nearly all light and medium-sized enemy tanks. Reportedly able to compromise and KV-1 and IS-2, but only quote sources.
Versions
 |
| 2.8 cm sPzB 41 Basic version |
2.8 cm sPzB 41 Basic version,Type - schwere Panzerbüchse
Year of origin - 1940 Produced - 1940 to 1943 In service - 1941 to 1945
Producer - Mauser Werke AG, Oberndorf am Neckar
Produced - 2.797 pcs
Weight - 229 kg
Length - 2.690 mm
Barrel length - 1.730 mm
Width - 965 mm
Height - 838 mm
Service - 3
Caliber - 28/20 mm
-5 ° to 30 °
Azimut - 70 °
Rate of fire - 30 rounds per minute
Sped - 1.400 m / s
Range 500 m
2.8 cm sPzB 41 leFl 41 (2.8 cm schwere Panzerbüchse 41 auf leichterfeldlafette 41)
 |
| 2.8 cm sPzB 41 leFl 41 |
- Version developed for the Airborne units. Used a lightweight chassis with no suspension, wheels were reduced and peak was mostly detached. The resulting weight was 139 kg (118 kg without the travel). Chassis allows measuring 360 ° and measured from -15 ° to 25 °.
2.8 cm KwK 42
modification. 24 pieces were produced. It is unclear whether they were ever used outside of testing. sPzb 41 is mounted on SdKfz 250/11. Some pieces were mounted on armored vehicles SdKfz 221
Ammunition
 |
| Ammunition |
There are two types of ammunition designed for the 2.8 cm sPzB 41
- 2.8 cm penetrating Pzgr.41 Production of ammunition 512 600 pcs
- 2.8 cm cluster Sprg.41 with 5 g PETN (pentaerythritol tetranitrate, known as penthrite) Production of ammunition 1 602 800 pcs
Production of 2.8 cm sPzB 41
1940 94 pc
1941 349 pcs
1942 1030 pcs
1943 1324 pcs
Total 2797 pcs
2.8 Pzgr characteristics.
100m/60 ° / 52 (69) mm
100m/90 ° / 75 mm
300m/60 ° / 46 mm
400m/90 ° / 40 mm
500m/60 ° / 40 (52) mm