

Article fait par :Claude Balmefrezol
Mis en ligne le

U.S.S. Texas Le T Mighty
English Translation
 |
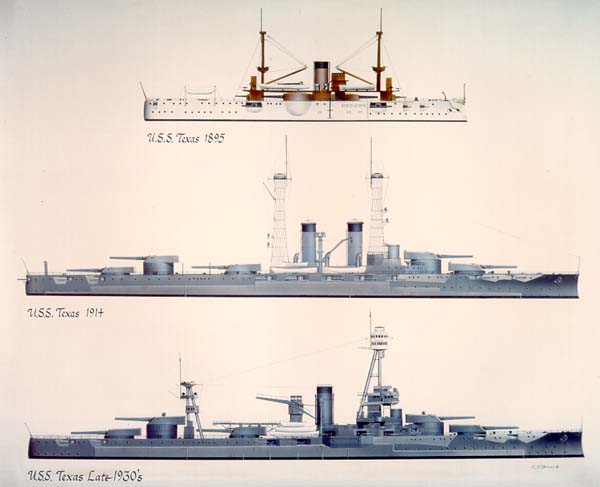
Le U.S.S. Le Texas est le dernier survivant Dreadnoughtdans le monde Ce cuirassé a été construit en 1914 et il a été mouillé aujourd'hui à coté du champ de bataille de San Jacinto State Historical Park à La Porte , Texas.
Ce fut le 2e cuirassé à porter ce nom
 |
USS Texas
.gif) |
(1).jpg) |
| Internet | Internet |
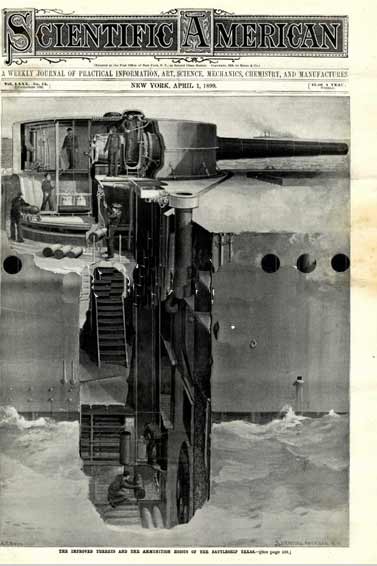
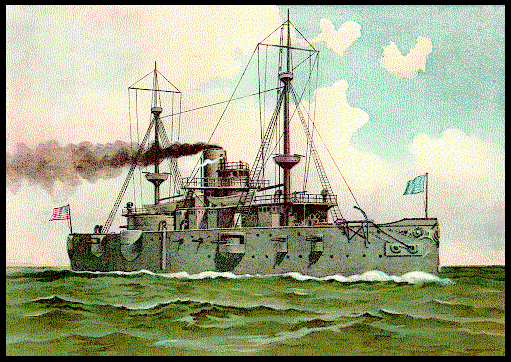
le premier USS Texas était le sister-ship de l'USS Maine. Sa construction a été autorisée par le Congrès des États-Unis le 3 août 1886, et il fut construit à partir de plans anglais dans les chantiers de l'US NAvy à Norfolk, en Virginie. Il a été commandé le 15 août 1895 .Il croise au large de la côte Est des Etats-Unis, et également dans le golfe du Mexique au début de la guerre américano-espagnole, durant laquelle il fait parti du "Flying Squadron" avec lequel il arrive à Cuba le 21 Février, 1898.
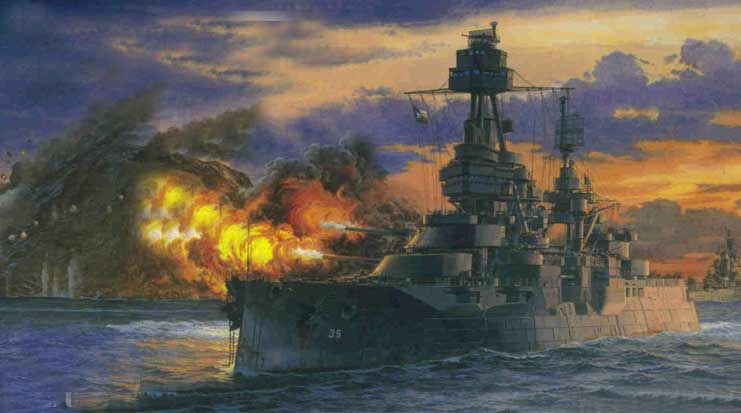
Il commence à patrouiller régulièrement en assurant le blocus L' USS Texas a pris part au bombardement de la forteresse sur Cayo del Tore, à Guantanamo Bay, à Cuba le 16 Juin 1898 Il endommage en l'incendiant le fort, au point qu'il ne fut plus une menace pour les forces américaines plus tard, Après le 3 Juillet , il prend une part active à la bataille de Santiago où il attaque quatre navires espagnols
Après la signature du traité de paix l'USS TEXAS retourne à New York le 31 Juillet 1989
Ensuite, il reprend ses patrouilles aux larges de la côte Nord-Est des Etats-Unis
 |
Il est brièvement mis en réserve en 1901 pour des réparations, mais remis en service le 3 Novembre, 1902. Il fut le fleuron du Costal Squadron" jusqu'en 1905, et ceci jusqu'en 1908. En 1908, il devient navire base à Charleston, Caroline du Sud.
Le 15e USS TEXAS Février 1911 a été rebaptisé USS SAN MARCOS, afin que l'ancien nom pourrait être donné à un nouveau cuirassé (BB-35).
Le 10 Octobre 1911. Il est coulé comme cible dans la baie de Chesapeake.
USS Texas BB35
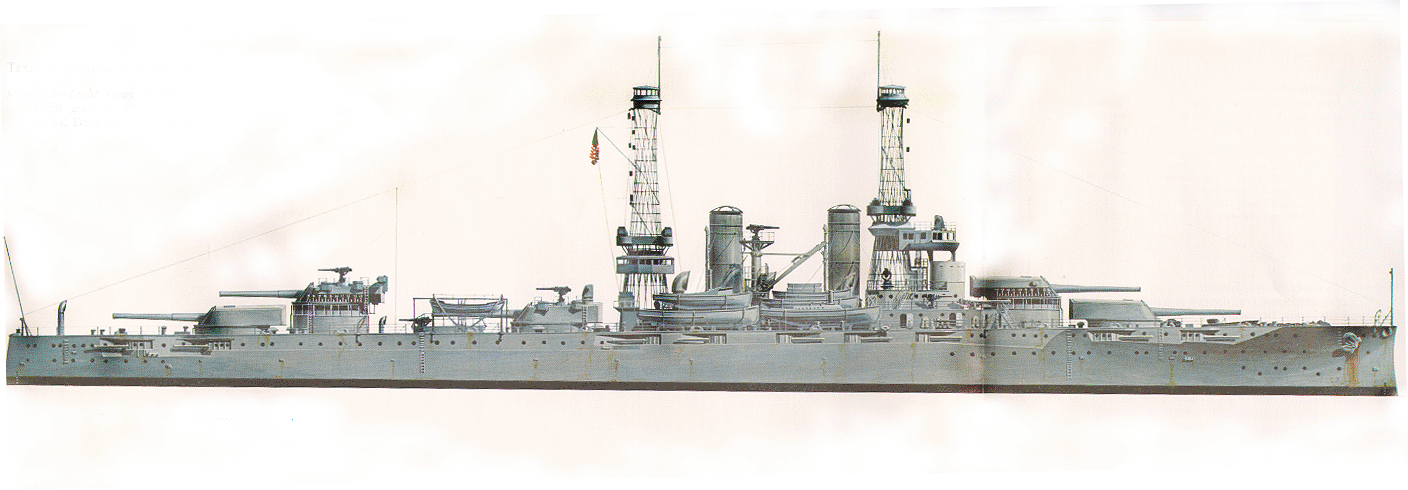 |
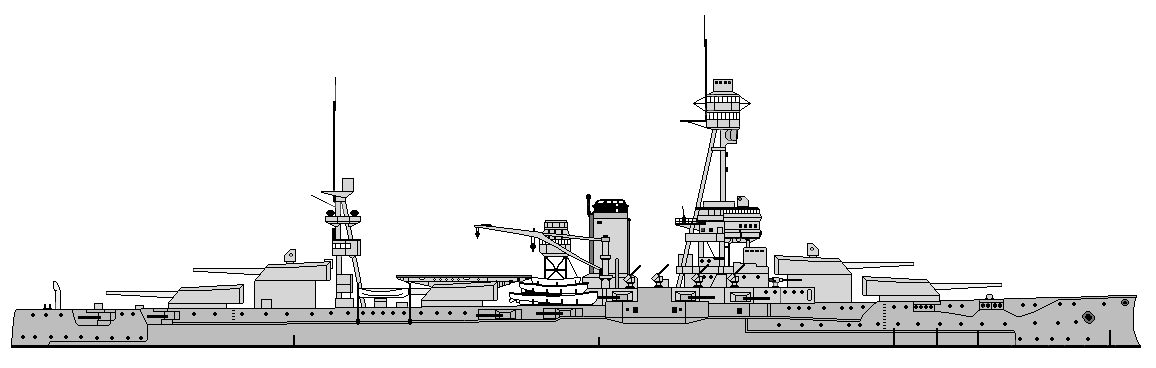
L' USS Texas était un Dreadnought construit à Newport News entre 1911-1914
C'etait un cuirassé de 31000 tonnes, et il est maintenant, le seul survivant Dreadnought dans le monde.
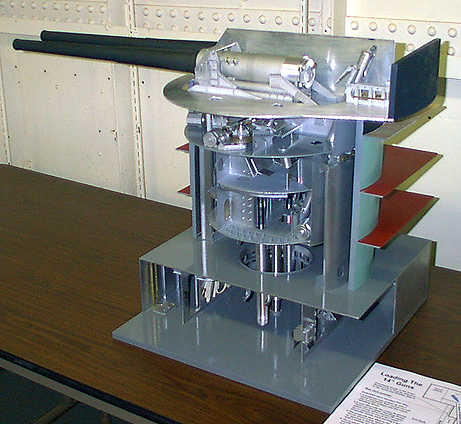
L''USS Texas fut le 4e cuirassé de la classe New York cuirassé Les USS Texas et New York ont été appelés super-Dreadnoughts car: ils étaient équipés de dix canons de 14 pouces (355 mm), et initialement de 21 canons de 5 pouces (127 mm) réduits à six
 |
 |
| Internet | Internet |
Comme les Dreadnoughts construits au depart les États-Unis, l'USS Texas ne possédait pas de turbine à vapeur mais un moteur à triple expansion, en configuration à double vis car les États-Unis à ce moment n'avaient de installations industrielles capable de produiresdes les turbines à vapeurC'est seulement avec la classe Nevada que l'USN a finalement adopté moteurs à turbine comme standard pour ses cuirassés
L'USS Texas a toujours été équipé sa vie entière dev son moteur d'origine qui lui offrait unevitesse deà 21 Noeuds.
La vie opérationnelle
L'USS Texas a eu une vie pérationelle longue et bien remplie.
D"s sa mise en service il a été affectée pour appuer les actions contre Pancho Villa dans le Mexique pré-révolutionnaire Le cuirassé y resta jusqu'au 6 Septembre,
En avril 1917, lorsque Etats-Unis déclarent la guerre l' USS Texas, passe l'année 1917 en ussurant la protection des navires marchands qui étaient souvent attaqués au canon par des sous-marins allemands en surface. Ensuite avec l'USS New York, il est envoyé renforcer la British Grand Fleet au sein du 4th Battle squadron à Scapa flow et ceci jusqu'à qu'après la reddition de la KaiserlicheAlle Marine (21Novembre 1918. )
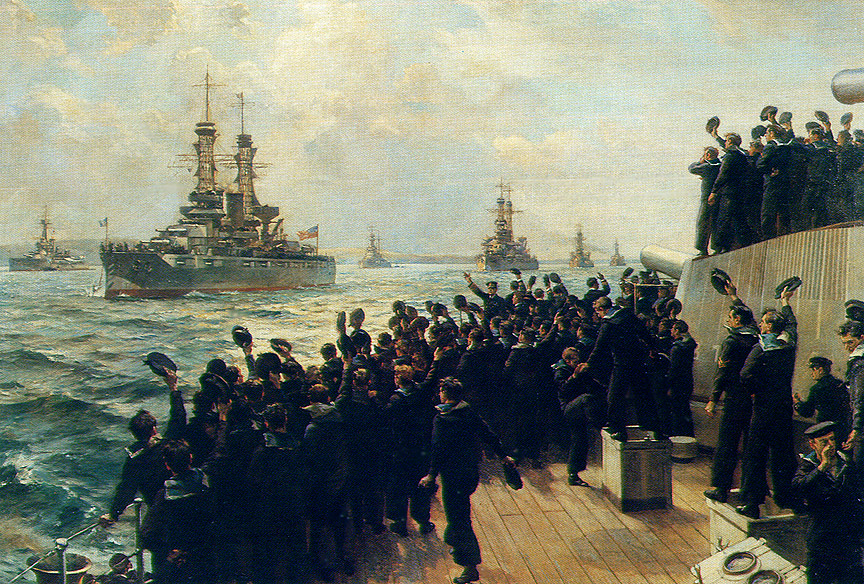 |
Le 20 Juin, 1919 les équipages allemands de la Kaiserliche Marine sabordent leurs propres navires internés à Scapa.. Il escorte le Président Wilson se reandant aux pourparlers de paix en France. Le 17 Juillet 920 il est rebaptisé BB-35 en suivant le nouveau sytème de numerotation adopté de la US Navy
C'est aussi à cette époque 'aube de l'ère de l'aviation, qui voit l'USS Texas étret le 1e cuirassé américain à voir s'envoler un avion en 1919.
La piste de décollage peut être incliné en élevant gros canons de la 2e tourelle.
 |
Plus tard, après remise en état, elle reçoit en 1926 et une catapulte placée sur la 3ème e plc" derrier ela cheminée Pour lancer l'avion la tourelle se place face au vent
Les avions servent àléclairage et aussi au relgage de tir afin de permettre une correction instantanée et précise de la bordée
L'avènement du radar d'acquisition de cible durant la Deuxième Guerre mondiale, rend cette focntion obsolète .
USS Texas, a été modernisé à plusieurs reprises
En 1926, il est transforné pour naviguer au fuel et il reçoit des mats robustes qui remplacent les pylônes le tout couplé à une nouvelle commande de direction de tir
Il reçoit également deux lance-torpilles blister (places le long des deux côtés )
lL'armement principal est aussi avec la disparition de la tourelle centrale et d'un grand nombre des canons secondaires . Enn effet les canons montés en dessous du pont principal sont généralement envahi par la mer et ne peuvent tirer en cas de mer forte
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| New York | New York |
Peu de temps après en Septembre 1939, l'USS Texas rejoint la Neutrality Patrol Plus tard, comme les États-Unis se dirigent vers un soutien plus actif de la cause Alliée , l'USS Texas commence la protection des convois Lend Lease avec des navires transportant du matériel vers le Royaume-Uni Il recoit le 1e radar commercial de l' US Navy en 1939
Lors de l'attaque japonaise sur Pearl Harbor, le 7 Décembre 1941, l'Uss Texas est stationné avec la flotte de l'Atlantique ancré dans la baie de Casco, Maine.
Peu de temps après la déclaration de guerre il se dirige vers l'Argentine pour sa 1e mission de guerre Apres cette première affectation l' USS Texas, escorte les convois entre 1942 1943, (d'abord entre l'Argentine et l'Angleterre jusqu'à la fin de Janvier 1942. Une fois cette tâche accomplie, il assure la protection des convois de navires marchands et de convois de troupes durant 6 mois à travers l'Atlantique
Il est le navire amiral durant l 'opératiojn Toch qui le trouve aux large des cotes Marocaines le 8 Novembre, Il doit assurer le le soutien feu des troupes debarquées . Apres le succés de cette opération il retourne aux USA le 16 Novembre pour une modernisation à Boston Navy Yard
Il recotr de nouveaux radars et plusieurs canons AA (54x40mm canons Bofors et 44x 20 mm Oerlikon.
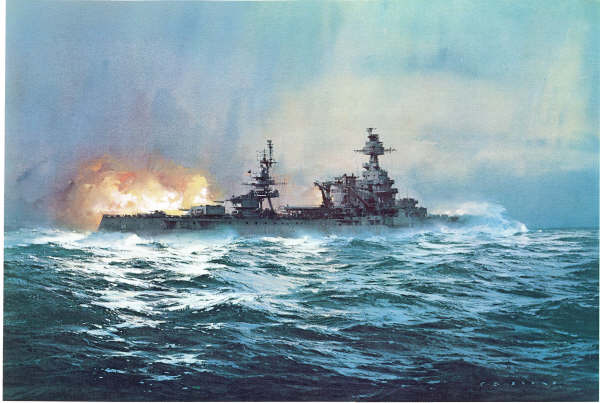
En 1944 il est à nouveau le navire amiral de la flotte de bombardement couvrant le D-Day ( invasion de la Normandie )
 |
 |
| Normandie | Cherbourg |
À la fin avril 1944, le Texas est de nouveau apte à soutenir les débarquements amphibies, prévue pour Juin 1944. . il arrive au large dela Normandie dans la nuit du 5 au 6 Juin. Pendant le débarquement' avec l' USS Arkansas,il apporte un appui-feu sur Omaha Beach et la Pointe du Hoc ; L'USS Nevada étant pour sa part en appui sur à Utah Beach Il appui les troupes mais doit revenir sur Plymouth, pour ravitailler le 8 Juin. il retourne au large des plages le 11 Juin pour un appui feu jusqu'au 15 Juin Les combats se sont alros déplacés trop loin dans les terres et les canons principaux ne peuvent plus apporter le soutien.
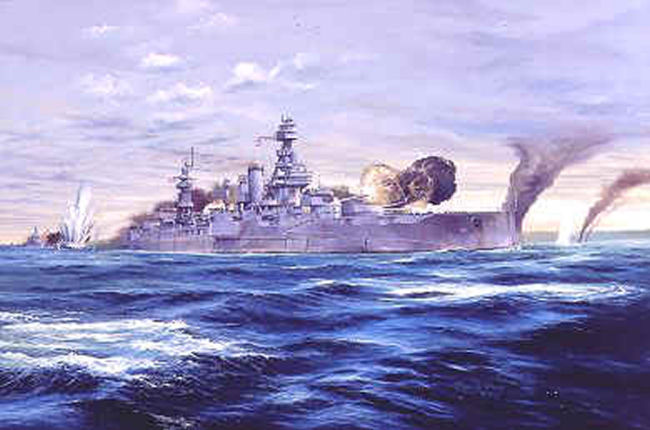
Il est affecté au bombardement des défenses de Cherbourg, odurant lequel il entame un duel avec la batterie allemande de Hambourg. durant lquel il touché par un obus de 280 mm Après réparation des dommages l'USS Texas part en Méditerranée pour soutenir l'invasion de la France méridionale, en bombardant les fortifications de St-Tropez. Il fourni un appui feu durant 2 jours et repart le 16 août.
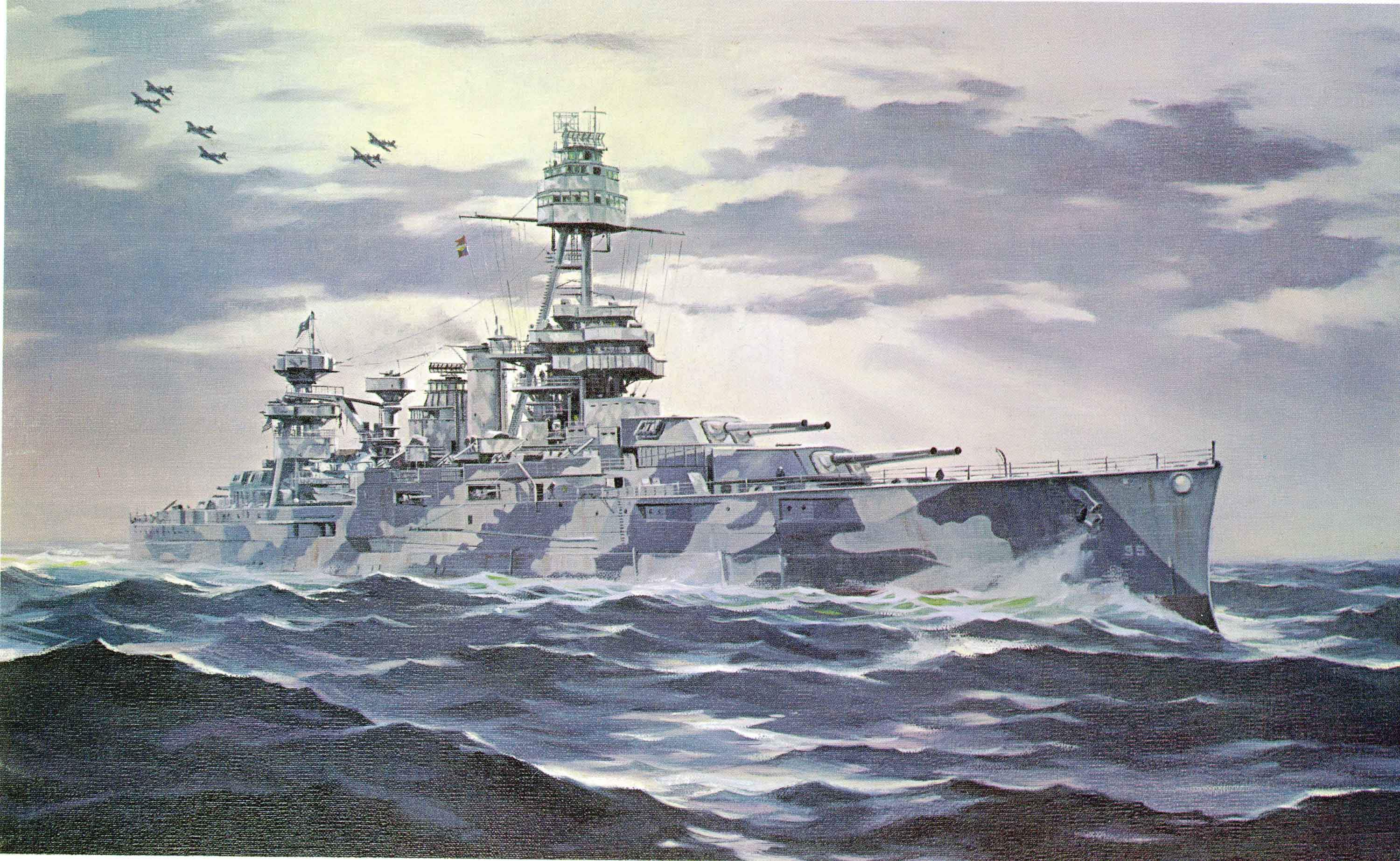
À la mi-Septembre, il se trouve à à New York pour réparationet période radoub. Il recoit un nouveau radar et lde nouveaux canons anti-aériens, mais la principale modification touche l'artillerie principale. qui a été très sollictée avec les bombardements en Europe, Les canons de 14 " sont très usés, Il recoit de nouveaux canons des Mark 12 14" Guns
A cette époque, il n'y avait guère besoin de cuirassés dans l'Atlantique alors il se dirige donc en Novembre pour le Pacifique via le canal de Panama avec l'Arkhansas et le Misssouri
Après une courte escale à Long Beach, en Californie, il part vers à Pearl Harbor, et ensuite il part l' Atool d' Ulithi et part le 16 Février 1945 avc le Nevada et l'Arkansa destination: Iwo Jima, où les Marines ont debarqués le 19 Févrie
 |
Il participe au bombadement du mont Suribachi. Plus tard, il prend part à l'invasion d'Okinawa, Durant cette mission il subit une attaque kamikaze Le 16 avril, 1945 dans le cadre de la Task Force 54, il part de l'Atool d'Ulithi le 21 Mars et cinq jours plus tard il commence le bombardement de la zone de debarquement durant les six jours qui précédent le débarquement et ensuite in fourni durant 2 mois un appui feu Bien qu'il y ait subit de nombreuse attaques kamikazes pendant l'opération, il en fut pas touché mais il a reussi a abattre un avion kamikaze A la fin de Mai, il part pour le golfe de Leyte aux Philippines pour réparation où il séjourne jusqu'à la fin des hostilités le 15 août.
Il retournée à Okinawa vers la fin du mois d'août et resté dans les parages du Ryukyus jusqu'au 23 Septembre.
L'USS Texas a la réputation d'être un navire chanceux car il a survécu à deux guerres mondiales avec des pertes minimes,
Ensuite durant 5 mois, le Texas prend part à l'opération «Magic Carpet», qui voir le retour des troupes US au pays .
Elle a obtenu cinq silver Battle pour services durant la Seconde Guerre mondiale.
Après 3 allers-retours, il retourne à Norfolk en 1946 et a été placé en réserve à Baltimore.
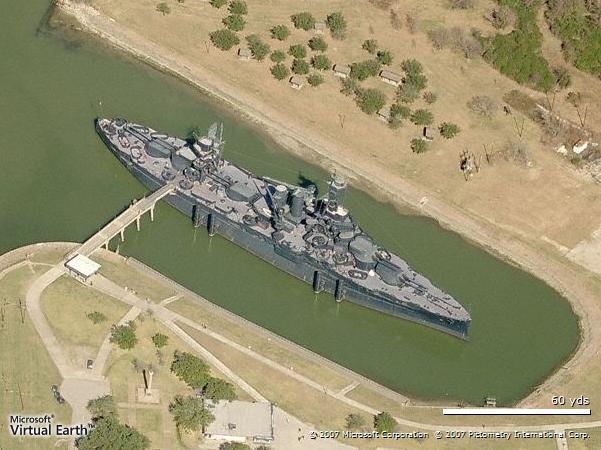
En 1948, elle a été remorqué jusqu'à l'est du Texas, radié des cadres de l'Us Navy mais il est rapidement remis en service comme navire amiral de la Marine du Texas. Il devient alors un mémorial de guerre permanent à San Jacinto State Park près de Houston.
.jpg) |
Données techniques 1914
Déplacement: 27.000 tonnes std; 28400 tonnes PC
Equipage: 58 officiers, 944 hommes
Dimensions:
Longueur 174 m
Largeur 29 m
Armement:
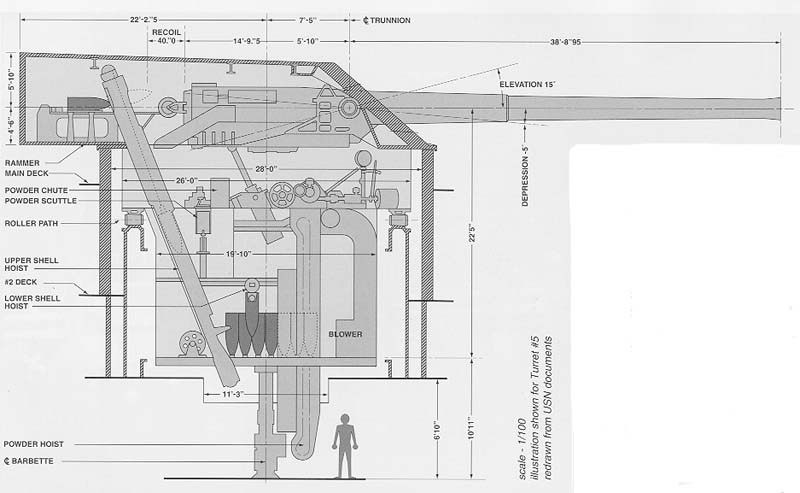
10 14 "/ 45 Cal. Mc. 8 (355 mm) dans 5 tourelles de 2
21 5 "/ 50 Cal. (127mm) dans des casemates et garnitures ouvertes;
8 3 "/ 50 Cal. AA 76 mm (car construit)
4 21 "tubes lance-torpilles.
Propulsion:
14 chaudières Babcock & Wilcox verticale à l'envers 4-cyl. machines à triple expansion
28000 SHP, défoncée à deux hélices.
Vitesse 39 km / h
Rayon d'action 17,779.2 km à 18.5 km / h; 6,852 km à 36 km / hr.
USS Texas 1944
Déplacement: 30,350 tonnes std; 34.000 PC.
l'équipage (1944): 98 officiers, 1625 hommes
Armement:
10X 14 "/ 45 Cal. Mc. 12 (5x2);
6 X 5 "/ 50 Cal. Gunhouse en armure;
10x 3 "/ 50 Cal. AA
40X 40mm Bofors AA
44X 20mm AA canons Oerlikon
Avion: (2) Vought-Sikorsky OS2U Kingfisher. avions ont été arrimés sur la catapulte ferroviaire lorsqu'il n'est pas utilisé
Capacité de fuel: 5200 tonnes de pétrole.
Propulsion:
6 Bureau Express chaudières. Original verticale à l'envers 4-cyl. machines à triple expansion, le développement de 28.000 SHP, défoncée à deux hélices.
Vitesse 38 km / h
Autonomie 15,400 Nm à 10 nds; 6500 nm à 18 noeuds.
 |
 |
| L' USS TEXAS |
Photoscope Walk Around ICI HERE
U.S.S. Texas The Mighty T
.jpg) |
The U.S.S. Texas is the last surviving Dreadnought in the world This battleship was built in 1914 and it was preserved now in the San Jacinto Battleground State Historical park in La Porte, Texas.
It is the 2nd battleship to carry this name
.jpg) |
USS Texas
 |
.jpg) |
| Internet | Internet |
the first USS TEXAS was the sister ship of the USS Maine . Her construction was authorized by the U.S. Congress on August 3rd 1886 She was built from English plans at the U. S. Navy yards at Norfolk, Virginia. She was commissioned on August 15th 1895 and became the first bonfied United States Battleship. She cruise off of the East Coast of the United States, and also in the Gulf of Mexico At the outbreak of the Spanish American War, she was assigned to the "Flying Squadron" and arrived off Cuba on February 21, 1898. She began regular patrolling and blockading duty. USS TEXAS took part in the bombardment of the fortress on Cayo del Tore, Guantanamo Bay in Cuba on June 16th 1898 Its fire damage the fort to the point that it was no longer a threat to the United States forces Later after on July 3, she took an active part in the Battle of Santiago where she attack four Spanish vessels
.jpg) |
After signing of the peace treaty USS TEXAS returned to New York on July 31st
Afterwards she again began patrolling generally off of the U.S.'s northeast coast
She was briefly decommissioned in 1901 for repairs, but recommissioned on November 3, 1902. She served as the flagship of the "Coast Squadron" until 1905, and continued to serve with the squadron until 1908. In 1908 she became a station ship at Charleston, South Carolina.
On February 15th 1911 USS TEXAS was renamed USS SAN MARCOS so that the old name could be given to a new battleship (BB-35).
On October 10th 1911. She was sunk as a target in Chesapeake Bay.
USS Texas BB35
USS Texas was a dreadnought built at Newport News between 1911-1914
She was a 31,000-ton battleship and now she was the sole surviving dreadnought battleship in the world.
USS Texas was the fourthof the New York class battleship, the first U.S. Navy dreadnoughts class USS Texas and New York were called super-dreadnoughts because: they mounte ten 14 inch guns(355 mm) a piece and, initially 21 5 inch guns (127 mm) later reduced to six
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Internet | Internet |
Like the early U.S. dreadnoughts, US Texas as not a steam turbine as powerplant but a triple expansion engine at tiwn screw configuration because USA has in this time limited facilities for machining steam turbines It was only with the Nevada Class that the USN finally adopted turbine engines as standard for its battleships
USS Texas was to live her entire service life with her original engine moving the ship at 21-kt speed.
Operational Life
USS Texas led a long and useful life.
When she was commissioned, she was assigned to assist in actions against Pancho Villa in pre-revolutionary Mexico. The battleship remained there until 6 September,
In April 1917,when USA declared war USS Texas , spent 1917 training gun crews for merchant ships that were often attacked by gunfire from surfaced submarines. And after with USS New York they were sent to reinforce the British Grand Fleet (4th Battle squadron ) then on duty in the North Sea.in Scapa flow where they witnessed the surrender of the German on November 21st 1918.
.jpg) |
But on on June 20, 1919 German crews of the Kaiserliche Marine scuttled their own ships interned at Scapa . She escorted President Wilson to peace talks in France. On 17 July1920 she was designated BB-35 under the Navy's newly adopted alpha-numeric system of hull classification symbol
But in this time and at the dawn of the aviation era,USS Texas was the first American battleship to fly off an aircraft in 1919.
From then through the mid-20s she sported a short inclined track over upon the 2nd turrert
The takeoff track could be angled by elevating the turret's great guns.
Later after refit, she receive in 1926 for 2 decades a catapult was attached over the top and port side of the 3rd turret between the funnel and the aft fire director tower or mainmast To launch, the turret would be trained abeam facing into the wind and plane shot offside by the catapult mark IV
Battleship and aircraft used to scout ahead and also to spot the fall of shot and radio back instructions to their ship's fire control, enabling instant and accurate correction "on the fly."
The advent of radar for target acquisition in WWII, combined with spotting aircraft reporting over the target zone, improved the accuracy of battleship gunnery by quantum leaps over the rangefinder-and-plotter systems in use during WWI and earlier.
USS Texas was updated several times
In 1926 she was converted to oil fuel in 1926, and she receive sturdy tripods who replace the lattice masts with, with an fire director station
She receive also a fat torpedo blister along both sides,
many of the 5" gun mounts were removed, and the 5" armament concentrated in an armored citadel on the command level because the guns mounted below the main deck were usually "washed out" and inoperable in any kind of windy or rough conditions. Soon after September 1939,USS Texas began operating on the Neutrality Patrol Later, as the United States moved toward more active support of theAllied cause, USS Texas began convoying ships carrying Lend Lease Materiel to the United Kingdom USS Texas received the first commercial radar in the U.S. Navy in 1939
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Internet | Internet |
When the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941, Texas was stationed in the Atlantic fleet and anchored in Casco Bay, Maine, for a brief rest period after a "neutrality patrol."
Soon after war broke out she sailed to Argentina and received her first war assignment First USS Texas, was used in convoy escort duty between 1942 1943 She escort first from Argentina to England in late January 1942. Once this was complete she patrolled near Iceland until March and then continued escorting both cargo and troop ship convoys for about the next six months throughout the Atlantic
She was the flagship for the Operation Torch invasion of Morocco. She arrived at the beaches on the morning of 8 November but did not provide a pre-invasion bombardment or even provide support when the landings were underway. But instead, for the next week she only attacked when the Army called in for direct fire support With the the success of Operation Torch, she departed the African coast on 16 November and returned to her convoy escort role which she continued to do in 1943.In late’43 USS Texas entered Boston Navy Yard for a refit
She receive new radars and more AA guns (54x40mm Bofors guns in twin and quad mount and 44x 20 mm Oerlikons in single mounts.
in 1944 she became the flagship of the bombardment fleet covering the D-Day invasion of Normandy
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Normandy | Cherbourg |
In late April 1944, Texas was again preparing to support amphibous landings, this time the invasion of Europe in June 1944. The training lasted for about a month and she arrived at Normandy on the night of 5/6 June. During the invasion, Texas, along with the battleship Arkansas, was to provide fire support at Omaha Beach, and Pointe du Hoc while Nevada was at Utah Beach She continued to support the troops until leaving to rearm in Plymouth, England, on 8 June. She returned off the beaches on 11 June and once again continued to provide support until 15 June when the fighting moved too far inland for her main guns to reach.
and after she was assigned to shell Cherbourg's defenses where she make a duel with the German Hamburg battery . She was hit during this duel by a 280 mm shell After repairing battle damage to her bridge, USS Texasgo to south to support the invasion of southern France, bombarding the fortifications at St-Tropez. But she provided only support for two days and withdrew on 16 August. By mid-September she was at New York for a repair/refit period. She receive he new radar and installation many more AA guns but the principal modification was the main artillery . Following all the bombardments in Europe, the ship's 14" gun barrel linings were determined to be badly worn, so she received a new set of Mark 12 14" guns
By this time, there was little need for battleships in the Atlantic so she set sail in November for the Pacific via the Panama Canal with the USS Arkhansas and Misssouri
.jpg) |
After a short stopover at Long Beach, California, she sailed to Pearl Harbor where she operated for about a month before moving on to Ulithi Atoll. And on 16 February 1945 destination: Iwo Jima where USMC land on 19 February Whit the other US Battleship SS Arkansas and Nevada shell bomb the cliffs of Mt. Suribachi . Later, she also took part in the invasion of Okinawa, downing an attacking kamikaze on April 16, 1945. As a part of Task Force 54, she departed Ulithi on 21 March and five days later she began the pre-landing bombardment. The bombarding continued for the next six days until the landings on 1 April. For the next two months, she provided fire support for the troops at Okinawa. Although there was a large number of kamikaze aircraft during the operation, none were successful in hitting Texas although she was able to claim one kamikaze kill and three assists. By late May, she concluded her duty at Okinawa and sailed to Leyte Gulf in the Philippines to be repaired where she remained until the war ended on 15 August. She returned to Okinawa toward the end of August and stayed in the Ryukyus until 23 September.
She has ar reputation of a fortunate ship, surviving two world wars with only minimal casualties,
For the next 5 months Texas took part in "Operation Magic Carpet," ferrying returning troops back to the States.
She was awarded five battle stars for her service in World War II.
After 3 round trips, she returned to Norfolk in 1946 and was placed in reserve at Baltimore.
In 1948 she was towed to East Texas, decommissioned by the U.S. Navy, and promptly recommissioned as the flagship of the Texas Navy. She was a permanent war memorial at San Jacinto State Park near Houston.
 |
Technical data 1914
Displacement: 27,000 tons std; 28,400 deep laden:
Crew: 58 officers, 944 enlisted men:
Dimensions:
Length 174 m
Beam 29 m
Draft 8.7m '
Armament:
10 14"/45 cal. Mk. 8( 355 mm) in 5 turrets of 2
21 5"/50 cal. (127mm) in casemates and open mountings;
8 3"/50 cal. AA 76 mm (as built)
4 21" torpedo tubes.
Propulsion:
14 Babcock & Wilcox boilers vertical inverted 4-cyl. triple expansion engines
28,000 SHP, shafted to twin screw.
Speed 39 km/hr
. Endurance: 17,779.2 km à 18.5 km/hr; 6,852 km à 36 km/hr.
USS Texas 1944
Displacement: 30,350 tons std; 34,000 tons deep laden.
crew (1944): 98 officers, 1625 enlisted men
Armament:
10X 14"/45 cal. Mk. 12 (5x2);
6 X 5"/50 cal. in armored gunhouse;
10X 3"/50 cal. AA
40X 40mm Bofors AA
44X 20mm Oerlikon AA guns
Aircraft: (2) Vought-Sikorsky OS2U Kingfisher. aircraft were stowed on the catapult rail when not in use
Fuel capacity: 5200 tons oil.
Propulsion:
6 Bureau Express boilers. Original vertical inverted 4-cyl. triple expansion engines, developing 28,000 SHP, shafted to twin screw.
Speed 38 km/hr
Endurance: 15,400nm à 10 kts; 6,500nm à 18 kts.