


Doubs La Cluse et Mijoux Le Fort de Joux
English Translation
Merci à Christian Adams et à Jean marie Brams pour les photos
 |
| Fort de Joux ( Internet) |
 |
 |
 |
Introduction
Le Fort de Joux est édifié à l'entrée de la Cluse de Pontarlier commandant le passage reliant à travers le Jura la vallée de la Saône et la Bourgogne à la Suisse, les Flandres et la Champagne à l'Italie Cette grande voie commerciale se développe à partir du 13ème siècle, lors du renouveau des échanges européens,
Elle permet le transit des marchandises , la circulation des pèlerins C’est aussi une route stratégique qui a été un passage naturel à travers le Jura et ceci depuis l'Empire Romain.
Cette cluse a toujours constitué un verrou naturel d’où la présence des fortifications Après le rattachement de la Franche-Comté au royaume de France en 1674, le rôle joué par la place frontière de Joux devient capital dans la défense du "Pré Carré" de Louis XIV.
Historique
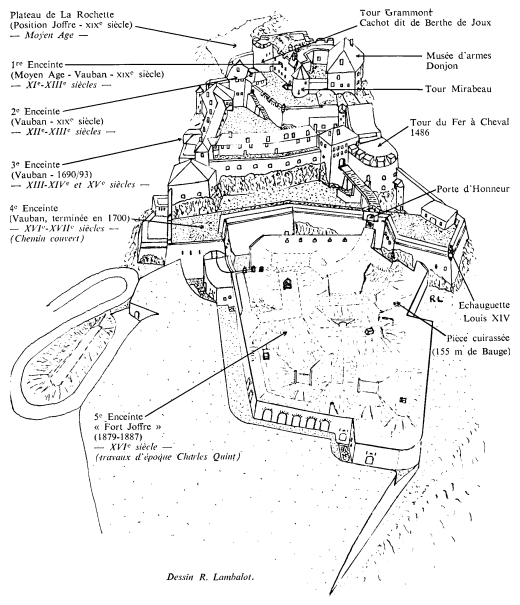
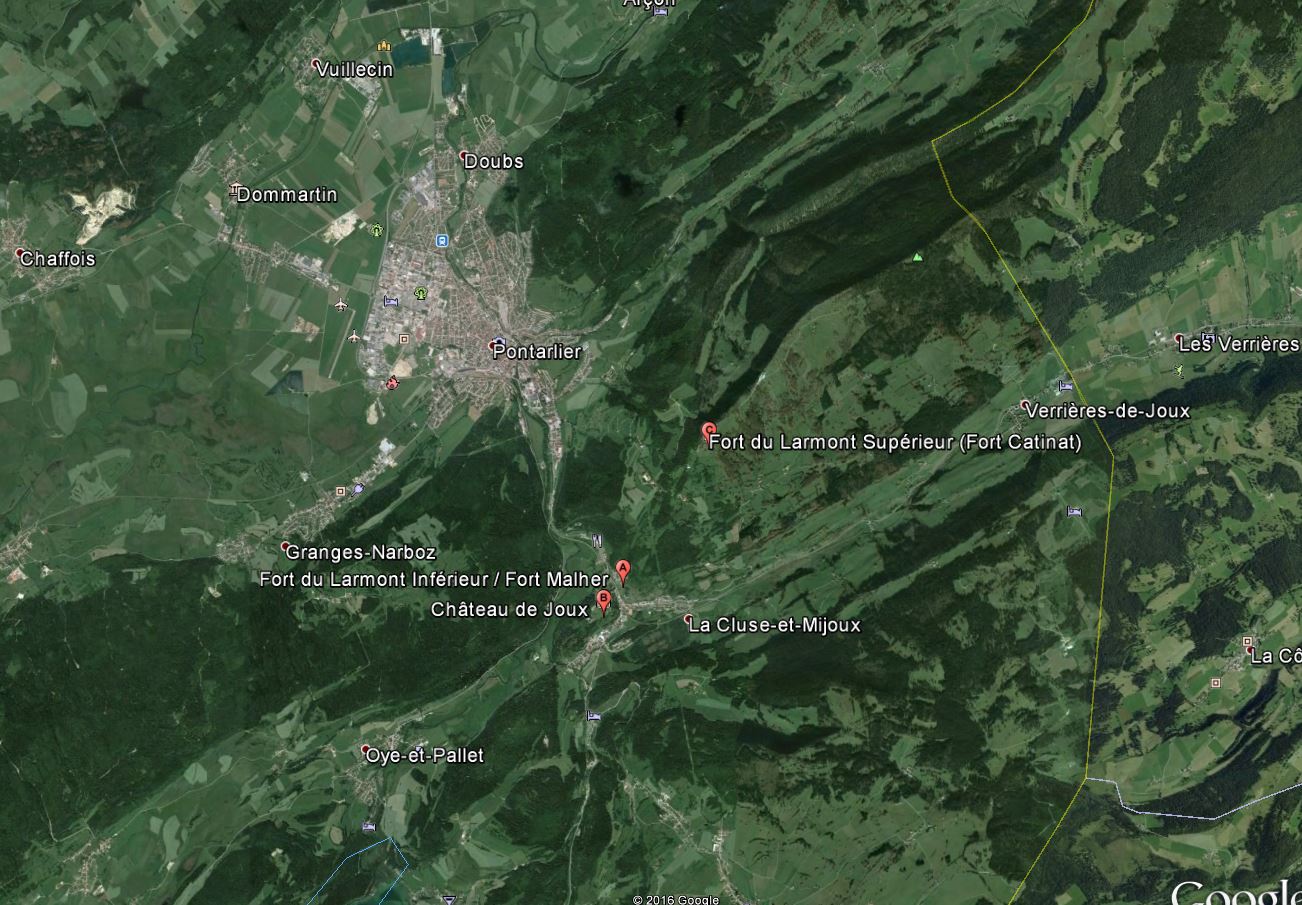
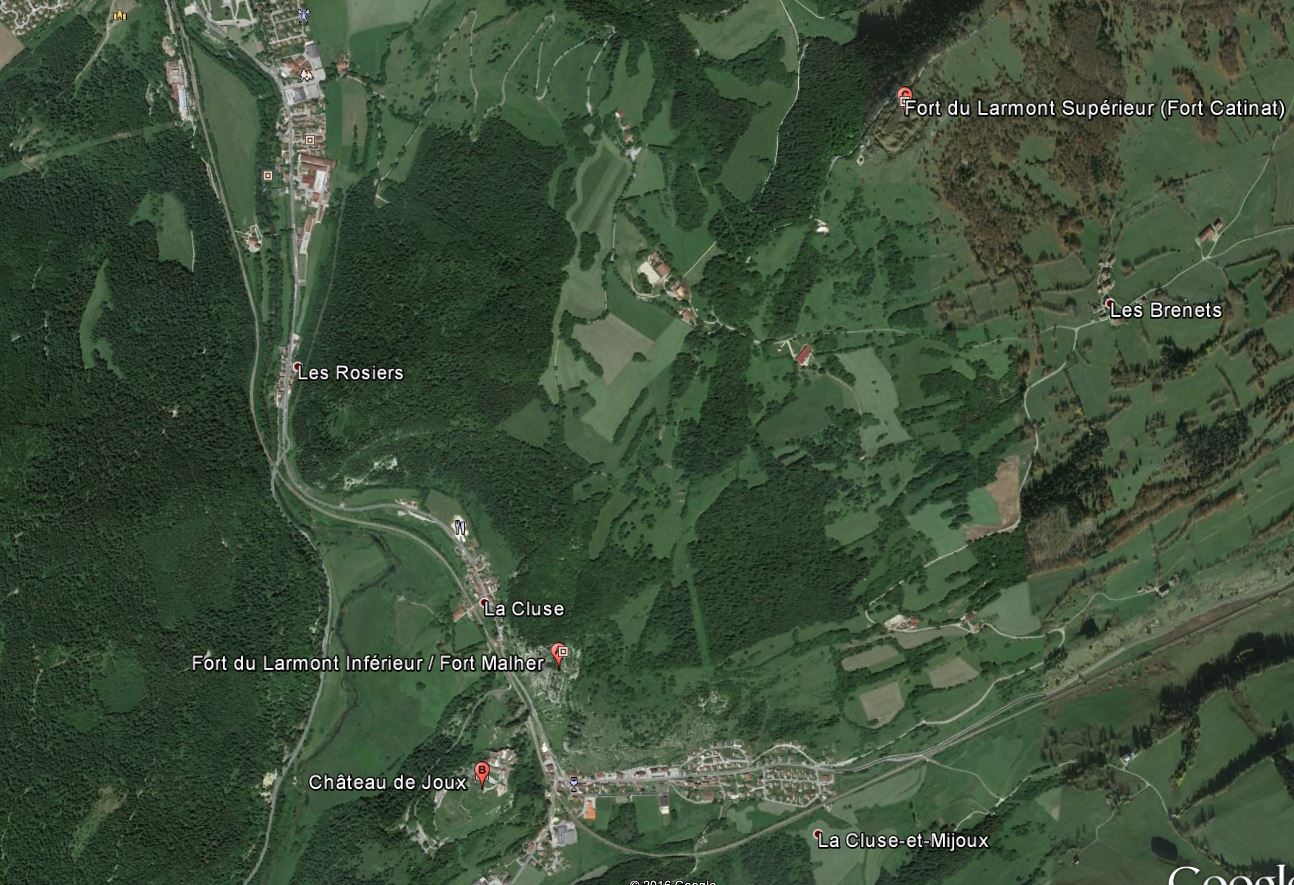
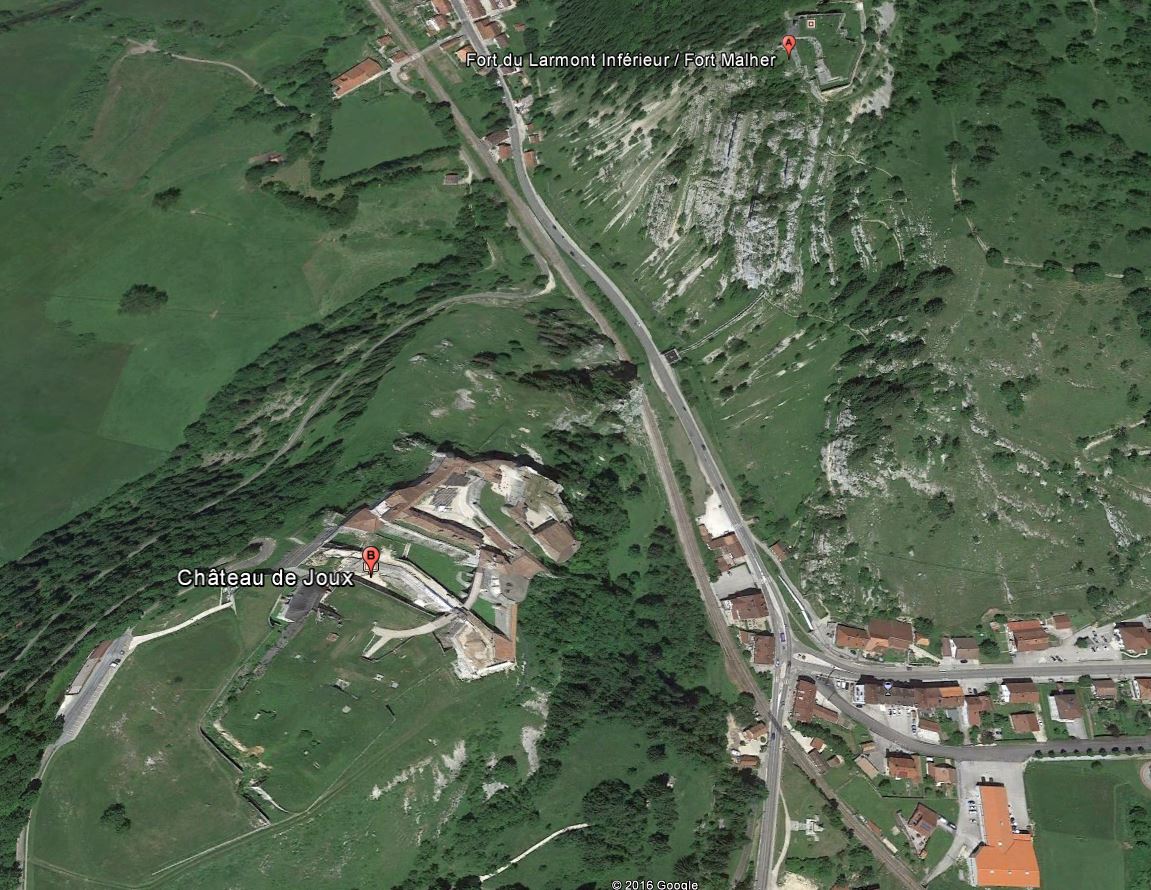
Ce fort surplombe la cluse de Pontarlier d’une centaine de mètres Il est construit à l'extrémité d'un promontoire toutefois les progrès réalisés par l'artillerie à partir du 17ème siècle entraîneront une évolution de la fortification avec l’ abandon progressif du plateau de la Rochette situé immédiatement au-dessus de la Cluse et renforcement des enceintes faisant face au plateau sud. Le fort Malher sera construit sur le Larmont entre 1844 et 1851. Plus éloignés de Joux, les forts du Larmont Supérieur et de Saint-Antoine datent des années 1880.
La légende
Comme tout nid d’aigle il y a une légende qui s’y rattache .Ici c’est la légende de Berthe de Joux qui se passe à la fin du XII° siècle
Berthe de Joux très jeune épouse du Seigneur Amaury de Joux voit partir son époux aux croisade Berthe, voit arriver 4 ans après autre sire, Amé de Montfaucon, qui se présente comme ayant participé à la même croisade et lui annonce la mort de son époux Berthe succombe vite au charme du nouveau venu. Mais une semaine après l'arrivée de Montfaucon, Amaury de Joux revint chez lui bien vivant. Fou de rage il fit enfermer Berthe dans un cachot d'1m3 creusé dans le mur d'une tour du donjon, aujourd'hui la Tour Grammont et pendre l'amant menteur .Berthe devait sortir 2 fois par jour de son cachot pour contempler le spectacle par une petite fenêtre. Après 12 années de captivité, le sire de Joux mourut et Berthe fut libérée. Elle se retira en l'abbaye voisine de Mont Benoît jusqu'à la fin de ses jours.
Retournons maintenant à la réalité
Construit sur des vestiges antérieurs un château en bois est mentionné dès 1034 car le château alors appelé Miroaltum ( qui voit haut ) est assiégé par Conrad II, empereur germanique et roi de Bourgogne mais la forteresse tomba finalement par surprise aux mains des Lombards du marquis Boniface. Il était alors connu sous le nom latinisé de Miroaltum que l'on retrouve dans les chartes médiévales ultérieures sous la forme de Miroaz, Mireval, Miroual, Mirouhaut,
La maison de Joux
En 1087, le seigneur Landri de Joux (Joux désignant primitivement des forêts de sapins le mot Jura serait la traduction latine de Joux ) est désigné "Castri jurensis possessor . Le château est alors reconstruit en Pierre en ce début du XII° siècle.il devient un puissant château fort dont il este comme vestiges la grosse tour Grammont et une partie du bâtiment du musée actuel
Les seigneurs de Joux Xème siècle-1326

Ces seigneurs ont favorisé la religion Vers 1130 l’abbaye de Mont Benoît fut richement dotée la transformant en une des plus riches abbayes du Haut Doubs. Les seigneurs de Joux bénéficièrent du droit de s'y faire inhumer. Amauri III de Joux se croisa vers 1170. Son fils Henri 1er(1196 à 1243 ) réserve Joux à son aîné Amaury IV qui le transmet à son fils aîné Henri II Mais la maison de Joux s'éteignit en 1326 avec lui

La sœur d’Henry de par son mariage avec Jean de Blonay, Jacquette de Joux eut un fils Hugues de Blonay, chevalier, seigneur de Joux, Mort très jeune, il laissa une fille prénommée Jeanne.
La maison féodale de Vienne1366-1454

Cette Jeanne de Blonay épousa Vauthier de Vienne qui mourut sans héritier en 1390. Sa veuve vendit la seigneurie en 1410 à Guillaume de Vienne, seigneur de Saint-Georges et de Sainte-Croix.Le fils de ce dernier, Guillaume II, ruiné, dut vendre ses seigneuries les unes après les autres. L'acquisition de Joux par Philippe le Bon, duc et comte de Bourgogne, en 1454, marqua la fin des sires de Joux proprement dits.
La Maison des comte de Bourgogne 1454-1480
Philippe le Bon fut sire de Joux jusqu'à sa mort (15 juin 1467). Son fils Charles le Téméraire lui succéda. Le 5 janvier 1477 sa fille, Marie, comtesse de Bourgogne, devint la nouvelle dame de Joux. Quelques mois plus tard (18 août 1477), celle-ci épousait Maximilien d'Autriche, fils de l'empereur Frédéric III.
Mais le château de Joux tomba aux mains de Charles d'Amboise le 27 avril 1480, sans combat, "grâce" à la trahison du capitaine de la place, qui avait reçu une somme de 13.000 livres.
La maison de Hochberg1480-1507

Louis XI rendit le château et la seigneurie à Philippe de Hochberg, comte de Neuchâtel Mais le jeux des alliances fait qu’à la mort de l'archiduc Philippe le Beau, l'empereur Maximilien craignit une invasion française de la Franche-Comté par les troupes de Louis XII s’empare de Joux en septembre 1507.
Joux domaine comtal 1507-1678

Le château et la seigneurie relèvent du domaine comtal et donc de la couronne espagnole Lors de la guerre de 10 ans en 1639 Les troupes "suédoises" de Bernard de Saxe-Weimar s’emparent de Joux et l’occupe jusqu'en 1648 date à laquelle Mazarin l’offre à Henri II d'Orléans, duc de Longueville, comte de Neuchâtel, descendant des Hochberg,
Mais en 1659 suite à la paix des Pyrénées le château revient au roi d'Espagne.
L'intégration au royaume de France1678-1789

Invoquant le droit de dévolution et le non-paiement de la dot de la reine Marie-Thérèse d'Autriche Louis XIV ordonna aux 20.000 hommes de Condé d'envahir la province en 1668. La conquête fut achevée en trois semaines. Le château de Joux se rendit sans combat. Le traité d'Aix-la-Chapelle (1668) ayant restitué la Franche-Comté à l'Espagne, il fallut une seconde conquête (1674) et la paix de Nimègue (1678) pour voir le Château définitivement associé au sort de la France.
Lieu de garnison important Joux abritait en permanence 600 soldats Des compagnies détachées de l'Hôtel des Invalides les remplacèrent à partir de 1715. Elles avaient surtout pour rôle de surveiller les frontières. En 1754, elles repoussèrent les troupes de contrebandiers menées par le fameux Mandrin .
Le château se transforma aussi dès lors en prison avec des personnages célèbres comme Mirabeau Toussaint Louverture
le château devient une forteresse frontière dont la garnison est commandée par un gouverneur.
Après la conquête de 1674, Vauban fait renforcer considérablement les défenses : reconstruction d'une partie du donjon, édification de l'ouvrage à corne formant la 4ème enceinte, creusement du grand puits de 120 mètres de profondeur, un des plus importants d'Europe et de profonds fossés taillés dans le roc. De nouveaux casernements abritent les troupes françaises en garnison à Joux.
Assiégé et pris en 1814 par les Autrichiens il sera renforcé par la construction des forts du Larmont inférieur et Larmont supérieur) durant le XIXe siècle
En 1871 il couvre la retraite de l’armée de Bourbaki vers la Suisse sous le commandant Ploton et ses 69 pontonniers qui inflige de lourdes pertes aux Prussiens (plus de 1.800 hommes hors de combat).
A partir de 1879 il fait partie du maillage de fort dits Séré de Rivières avec comme officier de génie un capitaine Joffre
La terrasse du donjon est adaptée, la 5ème enceinte bastionnée est remplacée par un "fort moderne" Une nouvelle entrée est réalisée en 1886-1887, après la crise de l'obus torpille.
Le fort accueille des canons de 155 mm, jugés comme les plus gros canons d'artillerie de l'époque dans deux casemates, «Mougin »complètement recouvertes sous plusieurs mètres de terre, mais aussi protégé par 4 de plaques en fonte de 20 tonnes chacune Un système de verrou à contrepoids permettait l'ouverture pour permettre le tir et des bouches d'aération permettaient aux gaz et poussières générés par le tir de s'évacuer rapidement.
Joux possède la seule casemate Mougin encore en état de fonctionnement
En 1940 le fort résiste 8 jours et ne capitule que le 24 juin, soit deux jours après la signature officielle de l'Armistice
En 1954, le fort commence a être visité en tant que monument historique sous la conduite de guides.Actuellement c’est un monument historique abritant un musée d'armes avec une collection d’armes allant du début XVIIIe au début XXe,
 |
 |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
Autre Photoscope (Other Walk Around ) 1
The Fort de Joux

Introduction
The Fort de Joux is built at the entrance to the Pontarlier Cluse who command the connecting passage through the Jura and the Saône Valley and Burgundy ,Switzerland, Flanders and the Champagne to Italy This great way trade grows from the 13th century, when new European trading,
It allows the transit of foods, movement of pilgrims is also a strategic road that was a natural pass through the Jura and this since the Roman Empire.
This cluse has always been a natural lock where the presence of fortifications After the joining to the Franche-Comté at the kingdom of France in 1674, the role played by this border fortification was apital in the defense of "Pré Carré" of Louis XIV.
History
This fort overlooks the cluse of Pontarlier form hundred meters and it is built at the end of a promontory, however, the progress made by artillery from the 17th century will lead to development of the fortification with the phasing of abandonment of the plateau de la Rochette located immediately above the Cluse and strengthening surrounding walls facing the South plateau . Fort Mahler will be built on Larmont between 1844 and 1851. Farthest from Joux, the forts of Larmont Superior and Saint-Antoine date from the 1880s.
The legend
Like any eagle nest there is a legend associated with it. Here is the legend of Berthe de Joux is happening at the end of the twelfth century
Berthe de Joux very young wife of the Lord Amaury de Joux see her husband go to Crusade After 4 years after other sire, Americ de Montfaucon which presents itself as having participated in the same crusade and it announces the death of her husband Berthe quickly succumb to the charm of the newcomer. But a week after the arrival of Montfaucon, Amaury de Joux returned home alive. Mad rage he lock Berthe in a dungeon of 1m3 dug in the wall of a tour of the dungeon, now the Tour Grammont and hang the lover liar. Berthe went out 2 times a day of his cell to contemplate the show a small window. After 12 years of captivity, the Sire de Joux died and Berthe was released. She retired in the abbey near Mount Benedict until the end of his life.
Now back to reality
Built on the anteriors remains earlier of a wooden castle is mentioned once in 1034 because the castle then called Miroaltum (which is high) is besieged by Conrad II, German Emperor and King of Burgundy but the fortress finally fell by surprise at the hands of the Lombards of the Marquis Boniface . It was then known by the Latinized name of Miroaltum that found in medieval charters later in the form of Miroaz, Mireval, Miroual, Mirouhaut,
The Joux Dynasty

In 1087, Landri lord of Joux (the world Joux originally designating fir forest in Jura and is the Latin translation of Joux) is designated "Castri jurensis possessor. The castle was rebuilt in stone at the beginning of the twelfth and he become a powerful castle which remains are the Grammont big tower and part of the building sheltering the actual museum
The Lords of Joux Xth century-1326
These lords have promoted Catholic religion .Towards 1130 the abbey of Mont Benedict was richly endowed transforming it into one of the wealthiest abbeys of Haut Doubs. The Lords of Joux enjoyed the right to make burial. Amauri III de Joux is go to the crusades to 1170. His son Henri 1st (1196 to 1243) reserve Joux to Amaury IV her eldest which transmits it to his eldest son Henry II But the Joux dysnasty died with him in 1326
The Dynasty of Blonay1326-1366

Jacquette de Joux the sister of Henry from his marriage with Jean de Blonay, had a son Hugues de Blonay, knight, lord of Joux, Died very young, he left a girl named Jeanne.
The feudal Dynasty of Vienne1366-1454

This Jeanne de Blonay married Vauthier of Vienna who died without an heir in 1390. His widow sold the lordship in 1410 to William of Vienna, Lord of Saint George and Saint Croix. This son, William II, ruined, had to sell his lordships one after the other. The acquisition of Joux by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy and Count in 1454, marked the end of sires de Joux themselves.
The Dynasty of Earl of Burgundy 1454-1480

Philip the Good was sir of Joux until his death (June 15th 1467). His son Charles the Bold succeeded him. On January 5th 1477 his daughter, Mary, Countess of Burgundy, became the new Lady of Joux. A few months later (August 18th 1477), latter she married Maximilian of Austria, son of Emperor Frederick III.
But the chateau of Joux was keep by Charles d'Amboise on April 27th 1480, without fight, thank to the betrayal of the square Captain, which had received a sum of 13,000 pounds.
The Dynasty of Hochberg1480-1507

Louis XI return the castle at the lordship oat Philip of Hochberg, earl of Neuchatel But with the alliances games at the death of Archduke Philip the Handsome, Emperor Maximilian feared French invasion of Franche-Comte by Louis XII troops seized Joux in September 1507.
Joux Counts property 1507-1678

The castle and the lordship are in the counts property and also of the Spanish crown during the War of 10 yearsIn 1639 "Swedish Troops " of Bernard of Saxe-Weimar captured Joux and held until 1648 when Mazarin offer the castle at Henry II of Orleans, Duke of Longueville, earl of Neuchatel, descendant of Hochberg,
But in 1659 following the Peace of the Pyrenees Castle returns to the King of Spain.
The integration in the Kingdom of France1678 1789

Citing the right of devolution and non-payment of dowry of Queen Maria Theresa of Austria Louis XIV ordered at Condé and his 20,000 men to invade the province in 1668. The conquest was completed in three weeks. Joux surrendered without a fight. The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668) give back the Franche-Comte to Spain, and it took a second conquest (1674) and Peace of Nijmegen (1678) to see the castle definitively linked to the fate of France
Joux was an important garrison housed permanently by 600 soldiers Companies detached from the Hotel des Invalides replaced them from 1715. They were mainly role to watch the borders. In 1754, they push back troops smugglers led by the famous Chuck.
The castle was transformed also in prison with celebrities as Mirabeau Toussaint Louverture
Castle was now a border garrison commanded by a governor.
After the conquest of 1674, Vauban is considerably strengthen the defenses: reconstruction of part of the tower, digging of a well of 120 meters deep, one of the largest in Europe and deep ditches carved into the rock. New barracks housing the French troops in garrison at Joux.
Besieged and taken in 1814 by the Austrians will be strengthened by the construction of forts Larmont inférieur and Larmont supérieur) during the nineteenth century
In 1871 it covered the retreat of the army Bourbaki to Switzerland under the commander Ploton and its 69 Pontoniers which inflicts heavy losses on Prussians (over 1,800 men out of combat).
From 1879 it is part of the Séré of Rivers system an he received as enginner officer the captain Joffre
The terrace of the dungeon is suitable, the 5th bastioned wall is replaced by a "very modern" A new entry is made in 1886-1887, after the crisis of the torpedo shells.
The fort received 155-mm guns, considered as the biggest artillery guns of the time in two bunkers, "Mougin" completely covered under several meters of land, but also protected by 4 plates cast of 20 tonnes each
A lock allow the opening counterweight to the shooting and vents allowed gas and dust generated by the fire quickly evacuated.
Joux has today the only bunker Mougin still in operation
In 1940 the fort resists 8 days and surrendered only on June 24, two days after the official signing of the Armistice
In 1954, the fort began to be visited as a historical monument under the guides.
Currently it is a historical monument housing a weapons museum with a collection of weapons from the early eighteenth early twentieth,