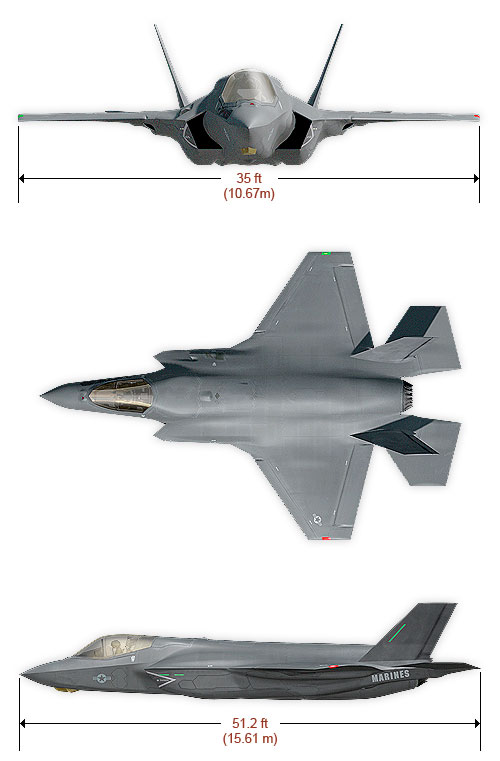
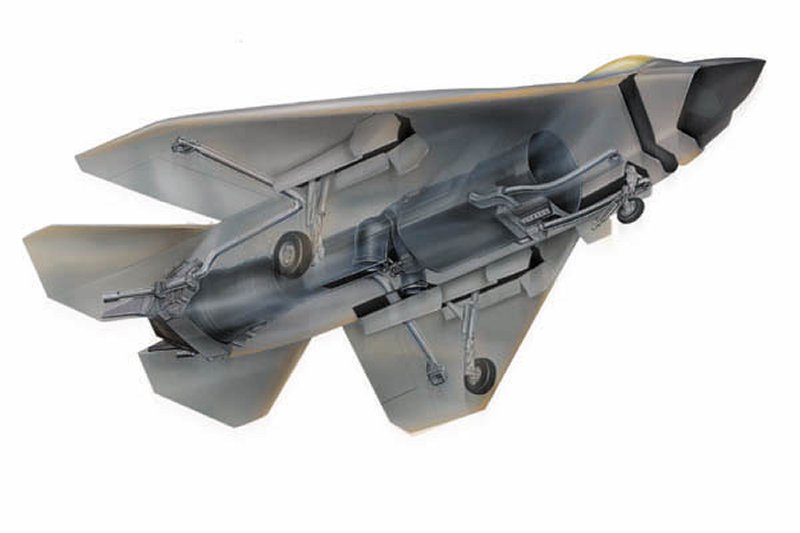
F-35 Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) Lightning II Prototype
English Transaltion
 |
En Novembre 1996 a commencé le programme JSF avec une concurrence entre Lockheed Martin et Boeing, pour déterminer qui sera le vainqueur .
Le 26 Octobre 2001 le Pentagone a annoncé que Lockheed-Martin a été le gagnant du concours avec un possible contrat de $ 200 milliards de dollars pour construire le Joint Strike Fighter.
Le coût total de ce contrat est de 19 milliards de dollars. Pratt et Whitney lui empoche un contrat de $ 4 milliards de dollars pour concevoir et construire des systèmes de propulsion de l'avion . British Aerospace contribuera à hauteur de 2 milliards de dollars pour le programme. Lentement le JSF est devenue un programme multinational avec l'US Air Force, US Navy, USMC, et d’autres partenaires internationaux.
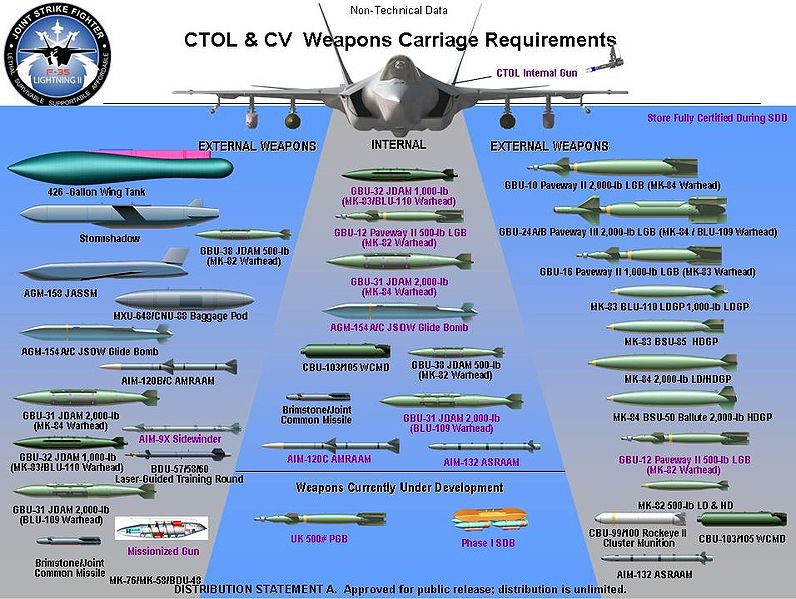
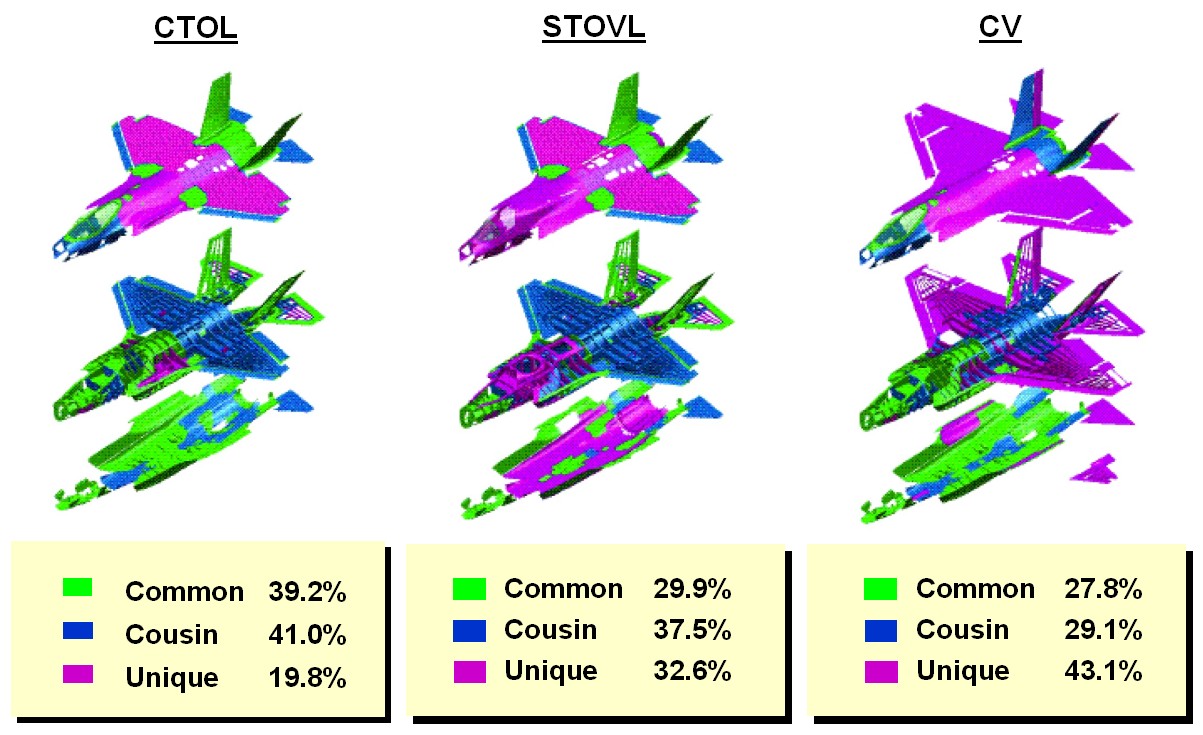
Ce avion furtif, supersonique le F-35 Joint Strike Fighter (F-35) va remplacer une large gamme d'avions de combat et d’attaque dans l'USAF US Navy, US Marine Corps et certaines forces aériennes dans le monde entier. La caractéristique du programme est de réaliser par le biais d'un prix abordable un avion en 3 versions:
conventionnelles de décollage / atterrissage (CTOL conventional takeoff/landing)
Version navalisée (CV carrier variant)
décollage court / atterrissage vertical (STOVL short takeoff/vertical landing )
a fabrication va s »étaler jusqu’en 2026 et éventuellement au-delà et cet avions devra rester en service jusqu'en 2060 ou plus.
Histoire
Le Programme Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) est l'ancien Joint Strike Advanced Technology Program (JAST) C’est un programme du Département de la défense pour la définition d'une prochaine génération d'avions d’attaque pour l’US Navy, l’USAF ,l’ USMC en premier et après pour les autres pays ( 2009 / 8 partenaires) le JSF remplira les taches suivantes en remplaçant
Dans l’US Navy avions de combat F/A-18E/F
USAF avion multi rôle (attaque-air-sol) pour remplacer le F-16 et A-10 et de compléter les F/A-22
USMC STOVL à remplacer les avions AV-8B et F/A-18 seulement comme Strike Fighter
Après le Royaume-Uni a besoin pour la Royal Navy et la RAF d’un appareil STOVL pour remplacer GR.7s & Sea Harrier comme une avion d’attaque supersonique
Pour les autres pays il devrait remplacer les F-16, F/A-18, AV-8B
En 1996 2 entreprises se sont vue attribuées un contrat d'une valeur d'environ $ 660 millions pour le Joint Strike Fighter Concept Boeing et Lockheed Martin Le marché prévoient de construire un avion capable de démontrer trois exigences
Possibilité de intercommunalité
Approche à basse vitesse et de qualités d’emport
STOVL vol stationnaire et transition entre les vols classiques et vol verticaux.
Les sociétés doivent aussi proposer un système d'armes
Nous trouvons donc en lice lea XF 32 de Boing et XF 35 de Lockheed-Martin
Le XF 32
Le X-32 possède une grande entrée d'air sous le cockpit et une aile en une seule pièce en fibre de carbone composite Pour moi, ce modèle est étrangement laid pour d'autres cet avion dans sa forme générale et sa conception ressemble à certains drones ou UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) ou à un F 22 Raptor mais en plus grand
Les deux X-32 prototypes ont une aile delta, qui a été choisie pour minimiser les coûts de fabrication de production. Cet appareil dispose également d'un nouveau design avec une dérive classique appelée queue de Pélican queue. Cette dérive réduit le poids et 'améliore l'agilité. Mais au cours de la phase developpe ment à la demande de l’US Navy Boeing est obligé de changer la forme de aile delta Les ingénieurs ne peuvent mener à bien leur tache car il est trop tard pour modifier les prototypes. Mais il a été jugé que cela serait suffisant pour démontrer la technologie de Boeing
En raison du poids de l’aile delta Boeing veut tester les vols STOVL et supersonique de façons différentes
La société soutient que la conception classique de la dérive n’’aura aucune influence sur les performances futures et que celle-ci ne nécessiterait pas de configurations distinctes.
Le premier vol de l'X32A a eu lieu en Septembre 2000 et pour les X32B premier vol en Mars 2001.
.jpg) |
Le X35
Le contrat pour le système de développement et de démonstration (SDD) a été signé le 26 Octobre 2001,
C’est un aéronef plus classique et contrairement au X32, il est capable de faire la transition entre le vol STOVL et supersonique en plein vol Au cours de la phase de développement X35 est trop lourd (8% 1000 kg), Lockheed Martin a ajouté de la poussée du moteur et de allège de plus d'une tonne l’avions en amincissement les tôles en diminuant la taille de la verrière
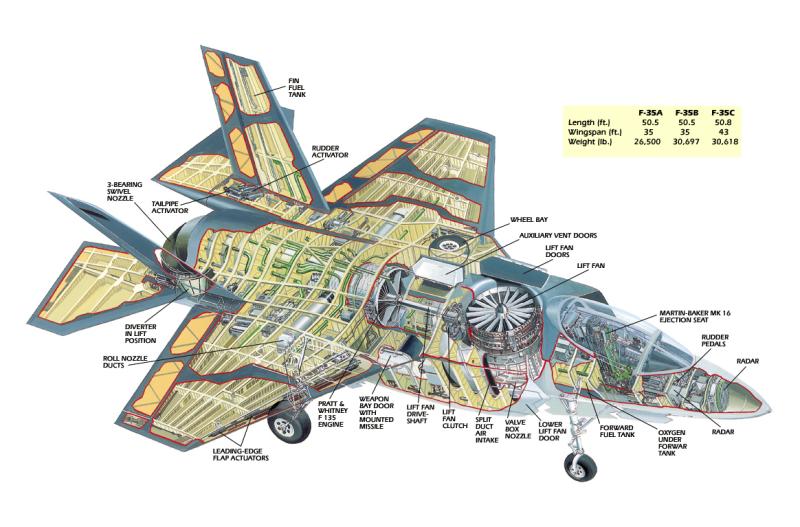 |
en octobre 2001 le X35 bat le X32. La désignation en tant que chasseur sera le F35 c’est une surprise parce que Lockheed, avait en tant que référence de cet appareil le F24
Le Lockheed Martin X-35 a été choisi par rapport au Boeing X-32 en raison principalement de la puissance de conception STOVL de Lockheed qui s'est révélée supérieure à la poussée vectorielle de Boeing
Le F35 sera donc le futur avion de combat furtif conçu pour répondre aux exigences du XXIe siècle pour l’US Air Force, l’ US Navy, et l’US Marine Corps et, ainsi que pour le Royaume-Uni, la Royal Air Force et la Royal Navy. Le programme a été international avec la participation de l'Italie, les Pays-Bas, la Turquie, le Canada, le Danemark, l'Australie et la Norvège
Pour les Etats-Unis, il a été élaboré à Fort Worth dans la société Lockheed Martin Corporation Lockheed-Martin travaille en équipe avec Northrop Grumman et British Aerospace
Le 7e Juillet 2006, l'US Air Force a officiellement baptisé cet avion Lightning II
Pourquoi ce choix Ce nom a été choisi en référence au P 38 Lightning célèbre avion de la 2e Guerre Mondiale et de l'avion britannique Electric Lightning Electric
Les Etats-Unis et les autres partenaires vont acheter un total de 2.443 JSF (prevision)
Versions
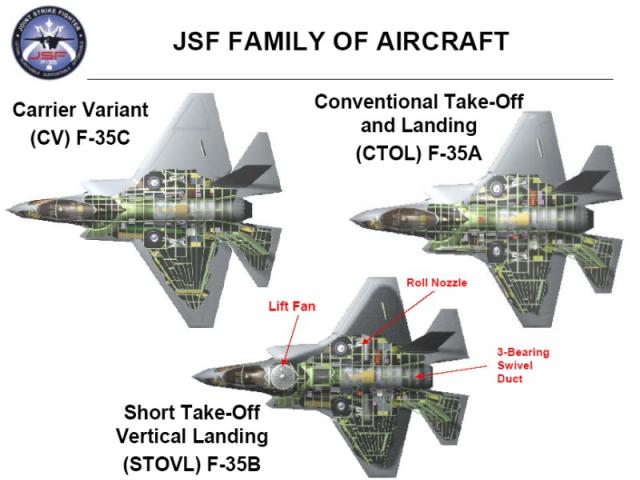
Le F-35 est prévu pour être construit en trois versions différentes pour répondre aux besoins de ses différents utilisateurs.
F35A
.jpg) |
F-35A est le décollage et atterrissage classiques (CTOL) Il est le plus petit, plus léger des version du F-35
Il a été équipé d'un canon GAU-22 / A. C'est un développement du 25mm GAU 12 adoptée par le USMC AV 8 B Harrier II
Il est agile et furtif il possède un désignateur laser interne et des capteurs infrarouges.
Il sera le successeur dans l'USAF des F16 en 2013, et A 10 Thunderbolt II en 2028.
F35B
F-35B c’est la version décollage court et atterrissage vertical (STOVL) version de taille similaire à la variante A, le B doit faire le sacrifice en volume de carburant pour faire de la place pour le vol vertical système. Car les décollages et atterrissages verticaux sont de loin les plus risqués,
Le F35B aura comme l’AV 8 B Harrier II à bord d'un pod ventral avec des canons
Il devra remplacer les F / A 18 Hornet et AV 8 B Harrier II USMC et 6b Prowler EA
Pour la RAF et la Royal Navy, il devra les Harrier GR 7 et le GR 9,
USMC a l'intention d'acheter 340 F-35Bs
F35B version est attendue en 2012.
F35C
.jpg) |
Le F-35C version navalisée devra remplacer le F/A-18A-BCD. Le F35C viendra appuyer le Super Hornet
Il est plus grand, ses ailes se plient et possède de grandes surfaces de contrôle pour améliorer le contrôle à basse vitesse, Il a un train d'atterrissage renforcé pour les contraintes de l’appontage . La plus grande surface alaire permet de vitesse d'atterrissage plus faible, et l'augmentation de portée et de charge utile, avec un emport presque du double d’armement et de carburant Cette version est attendue en 2015.
Les partenaires internationaux
Les neuf principaux pays partenaires prevoient d'acquérir plus de 3,100 F-35 jusqu’en 2035
Ils sont à différents niveaux de coopération Les niveaux reflètent généralement la participation financière dans le programme, le montant du transfert de technologie et de sous-traitance ouvertent aux des entreprises nationales, et l'ordre dans lequel les pays peuvent obtenir la production des avions. Les quatre premiers sont les plus importants
Niveau 1 USA
Niveau 2 Royaume-Uni (contribution de 2,5 milliards de dollars, environ 10% des coûts de développement)
Niveau 3 Pays-Bas en contribuant pour 800 millions de dollars américains et l’Italie, en contribuant pour 1 milliard $ US
Niveau l 4 Canada US $ 475 millions Turquie 195 millions $ Australie 144 millions $ Norvège US $ 122 millions Danemark 110 millions $ US
Niveau 5 Security Cooperative Participants (SCP): Israël et Singapour
Royaume-Uni
Royaume-Uni, doit acquérir 138 F-35Bs pour la RAF et la Royal Navy
Italie
Italie prévoit d'acquérir 131 avions de: 109 F-35As et 22 F-35B
Pays-Bas
Pays-Bas prévoit d'acquérir 85 F 35
Canada
Le Canada a été impliqué dans le programme Joint Strike Fighter Program de son début, en investissant 10 millions $ US pour être un "partenaire informé" pendant le processus d'évaluation
Turquie
La Turquie a prévu d’acquerir 116 F35A CTOL / L'avion sera produit sous licence en Turquie
Australie
L'Australie participe à la F-35 de développement, mais n'a pas encore placé une commande de l'appareil. Il est prévu de quelque 75 à 100 F-35As
Norvège
La Norvège prévoit de remplacer les F16
Danemark
Le Danemark a prévu de l'ordre de 48 F 35
Les participants de coopération de sécurité (SCP)
Israël
Israël a signé une lettre d'accord, la FIA besoin de 100 F-35A
Israël serait le premier pays étranger à recevoir le nouveau Fighter
Singapour
Singapour a rejoint le programme JSF System Design and Development (SDD)
Potentiel d'exportation
Inde
126 F35A pour la Marine de l'Inde qui a manifesté de l'intérêt pour le F-35B
Finlande
Pour le remplacement des F-18C Hornet décision sera prise vers 2015
Espagne
Pour la marine espagnole et le L 61 Juan Carlos I
Grèce
pour le remplacement de la F4E Peace Icarus 2000 et F-16C / D Block
 |
Utilisateurs Users (declarés)
.jpg) |
.png) |
.gif) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| USA |
Royaume Uni |
Italie |
Pays Bas |
Canada |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Turquie |
Australie |
Norvège |
Danemark |
Israël |
Autres Photoscopes (Others Walk Around ) 1 2 3 4
Voir Aussi Autre Photoscope See Also Other Walk Around
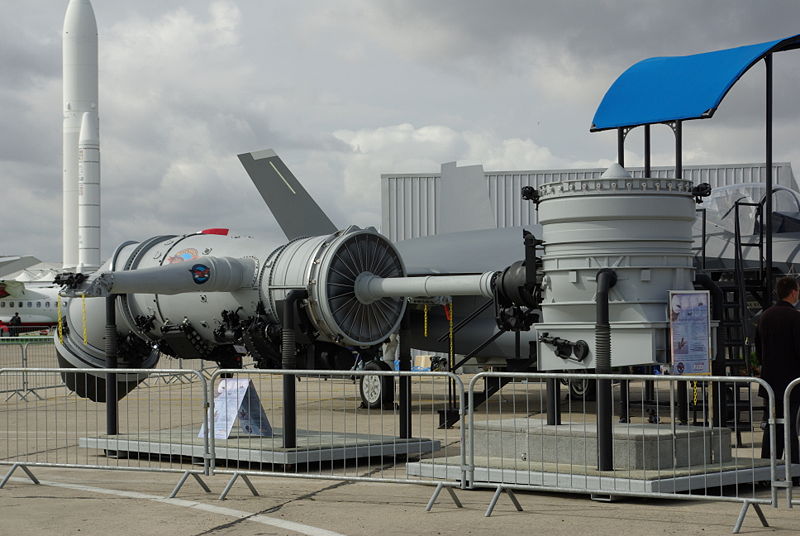
Réacteur Pratt & Whitney F135
F-35 Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) Lightning II Prototype
.jpg) |
In November 1996 began JSF program with a competition between Lockeed Martin and Boeing to determine the most capable and affordable preliminary aircraft design.
On October 26th 2001 Pentagon announced that Lockheed-Martin was the winner of the contest with a possible $200 billion contract to build the Joint Strike Fighter.
The total cost of this contract is $19 billion. Pratt and Whitney has a $4 billion contract to design and build propulsion systems for the craft. British will contribute $2 billion to the program. Slowly JSF became a joint, multinational acquisition program with USAF,US Navy, USMC, and eight cooperative international partners.
This stealth, supersonic F-35 Joint Strike Fighter (F-35) will replace a wide range of fighter and strike aircraft in USAF USNavy, USMarine Corps and allied defense forces worldwide. The program’s hallmark is affordability achieved through a high degree of aircraft commonality among three variants:
conventional takeoff/landing (CTOL),
carrier variant (CV)
short takeoff/vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft.
Procurement is planned to continue through 2026 and possibly beyond. JSF aircraft may well stay in service until 2060 or longer.
History
Joint Strike Fighter Program (JSF), formerly Joint Advanced Strike Technology Program (JAST) is a program of the Department of Defense for the definition of a next generation strike aircraft weapon systems for the USNavy, USAF, USMC first and after for other countries (2009 /8 partners)
JSF will fulfill stated Service needs as follows
US Navy strike fighter aircraft to complement F/A-18E/F
USAF Multirole aircraft (primary-air-to-ground) to replace the F-16 and A-10 and complement the F/A-22
USMC STOVL aircraft to replace the AV-8B and F/A-18 as only strike fighter
After United Kingdom need for Royal Navy and RAF a STOVL aircraft to replace Sea Harriers & GR.7s as a supersonic strike fighter
For other Countries replace F-16, F/A-18, and AV-8B
In 1996 2 contractors were awarded with a contract worth approximately $660 million for the Joint Strike Fighter Concept Demonstration Program The adwarded were Boeing and Locheed Martin The contract provide to build an aircraft able to demonstrate three specific requirements
commonality
low-speed handling qualities and carrier approach
STOVL hover and transition between conventional and vertical flight.
Contractor will be also propose weapon system designs
We found the XF 32 from Boing and XF 35 from 2 Lockheed-Martin
The XF 32
The X-32 featured a large chin mounted air intake and a large one piece carbon fiber composite wing For me this design show an strange aircraft ugly for other his design ressemble at the design of some UAV (unmanned Aerial Vehicle) or a larger F 22 Raptor
The two X-32 prototypes have a delta wing design, which was chosen to minimize production manufacturing costs. This aircraft has also a new design with a conventional tail (called Pelican tail ). This tail reduced weight and improved agility . But during the delopment phase request of the Navy change and Boeing's delta wing design fell short of the new targets. Engineers put together, but it was too late to change the prototypes. It was judged that they would be sufficient to demonstrate Boeing's technology
Due to the heavy delta wing design of the prototypes, Boeing demonstrated STOVL and supersonic flight in separate configurations, with the STOVL configuration requiring that some parts be removed from the fighter.
The company promised that their conventional tail design for production models would not require separate configurations.
The first flight of the X32A took place in September 2000 and for the X32B first flying in March 2001.
.jpg) |
The X35
The contract for System Development and Demonstration (SDD) was awarded on October 26th 2001 to Lockheed Martin,
Is a more conventional Aircraft and contrary to X32 he was capable of transitioning between their STOVL and supersonic configurations in mid-flight During the development phase X35 was too heavy (8% 1000 kgs) so Lockheed Martin added engine thrust and shed more than a ton by thinning the aircraft's skin shrinking the weapons bay and vertical tails; rerouting some thrust from the roll-post outlets to the main nozzle; and redesigning the wing-mate joint, portions of the electrical system, and the portion of the aircraft immediately behind cockpit
in final on october 2001 X35 beat X32. The designation of the fighter as F35 came as a surprise because Lockheed, which had been referring this aircraft as F24
Lockheed Martin X-35 was chosen over the competing Boeing X-32 primarily because of Lockheed's lift-fan STOVL design, which proved superior to the Boeing vectored-thrust approach.
F35 wild be the future stealthy combat aircraft designed to meet the XXIe requirements of the US Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps, as well as the United Kingdom’s Royal Air Force and Royal Navy. The program was international with the participation of Italy, Netherlands, Turkey, Canada, Denmark,Australia and Norway
For USA he was developed in Fort Worth in Lockheed Martin Corporation works Lockheed-Martin teamed with Northrop Gruman and British Aerospace
On July 7th 2006, USAF officially christen this aircraft Lightning II
Why this choose This name was coosen in reference of the P 38 Ligthning WW2 famous aircraft and the British et English Electric Ligthning and USA would buy a total of 2,443 JSF
Versions
The F-35 is planned to be built in three different versions to suit the needs of its various users.
F35A
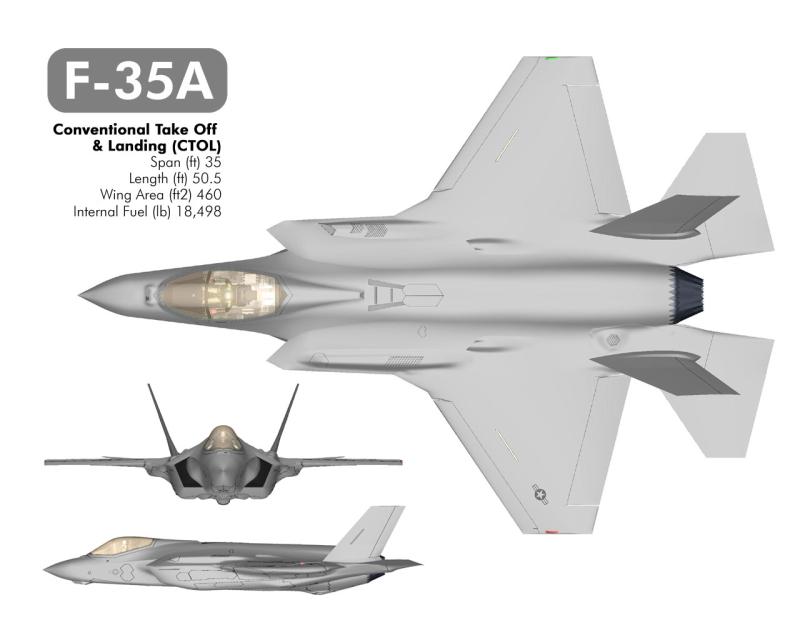 |
F-35A is the conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) versions It is the smallest, lightest F-35 version
He was equipped with an internal cannon, GAU-22/A. It his a development of the 25mm GAU 12 carried by the USMC'sAV 8 B Harrier II
He was maneuvrable and he has outperform it in stealth, payload, range on internal fuel, avionics, operational effectiveness, supportability and survivability.It also has an internal laser designator and infrared sensors.
He was the successor for USAF F16 in 2013, and A 10 Thunderbolt II in 2028.
F35B
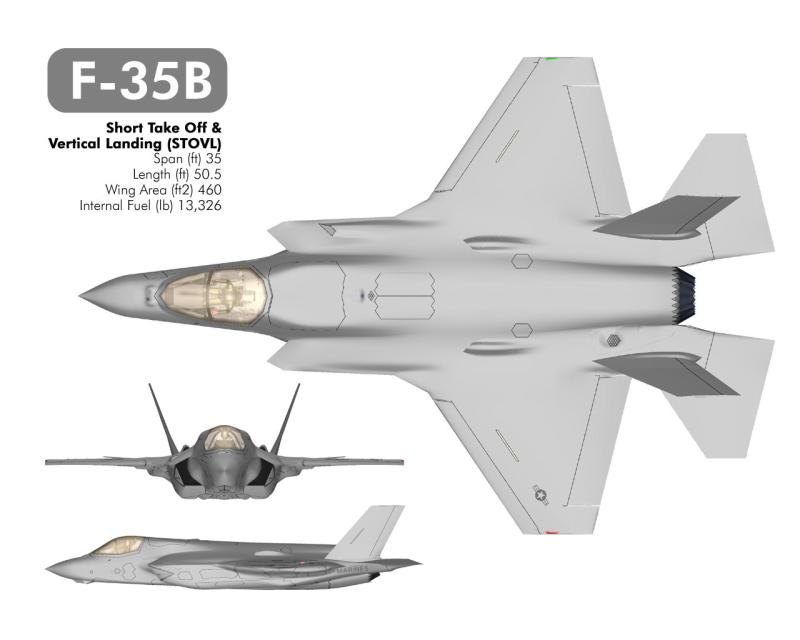 |
F-35B is the short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) version Similar in size to the A variant, the B sacrifices some fuel volume to make room for the vertical flight system. Takeoffs and landing with vertical flight system are by far the riskiest, and in the end, a decisive factor in design.
F35B like AV 8 B Harrier II carried in a ventral pod a gun
He would be replace F/A 18 Hornet and AV 8 B Harrier II in USMC and EA 6b Prowler
For RAF and Royal navy he would be replace Harrier GR 7 and GR 9,
USMC intends to purchase 340 F-35Bs
F35B version is expected in 2012.
F35C
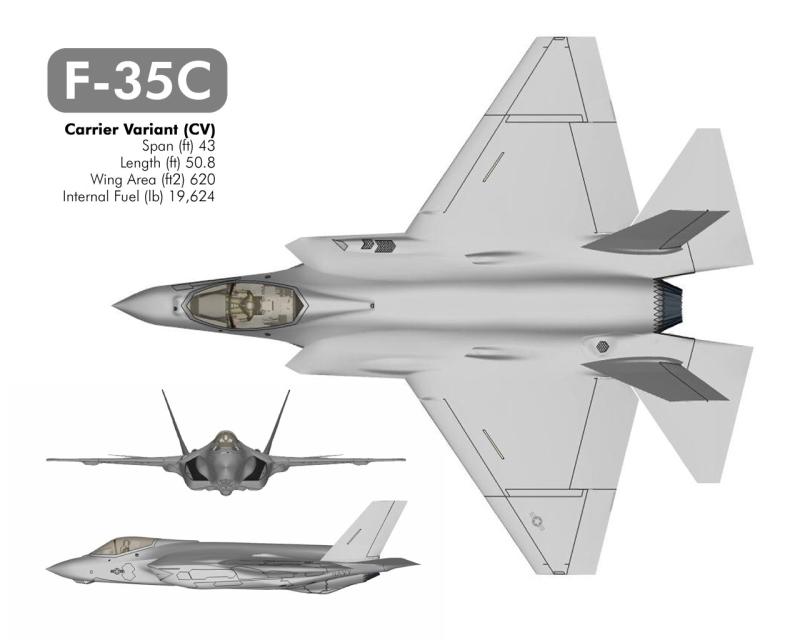 |
The F-35C carrier version is execpted to replace the F/A-18A-B-C-D .F35C will also serve as a stealthier complement to the Super Hornet
He has a larger, folding wing and larger control surfaces for improved low-speed control, and stronger landing gear for the stresses of carrier landings. The larger wing area allows for decreased landing speed, increased range and payload, with twice the range on internal fuel
This version is expected in 2015.
International partners
The nine major partner nations plan to acquire over 3,100 F-35s through 2035
They are differents levels in the cooperation The levels generally reflect the financial stake in the program, the amount of technology transfer and subcontracts open for bid by national companies, and the order in which countries can obtain production aircraft . The first four are the most importants
Level 1 USA
Level 2 UK (contributing US$2.5 billion, about 10% of the development costs )
Level 3 Netherland contributing US$800 million and Italy contributing US$1 billion
Level 4 Canada US$475 million Turkey US$195 million Australia US$144 million Norway US$122 million Denmark US$110 million
Level 5 Security Cooperative Participants (SCP): Israel and Singapore
United Kingdom
UK planned to acquire 138 F-35Bs for RAF and Royal Navy
Italy
Italy planned to acquire 131 of the planes: 109 F-35As and 22 F-35B
Netherlands
Netherlands planned to acquire 85 F 35
Canada
Canada has been involved in the Joint Strike Fighter Program from its beginning, investing US$10 million to be an "informed partner" during the evaluation process
Turkey
Turkey has planned for 116 F35A CTOL/Air Force versions the aircraft will be produced under license in Turkey
Australia
Australia is participating in the F-35's development, but has not yet placed an order for the aircraft. It is expected that some 75 to 100 F-35As
Norway
Norway planned to replace the F16
Denmark
Denmark has planned and order for 48 fighters
Security Cooperative Participants (SCP)
Israel
Israel signed a formal letter of agreement, IAF need 100 F-35A
Israel would be the first foreign nation to receive the new figther
Singapore
Singapore joined the JSF program's System Design and Development (SDD)
Potential exports
India
126 F35A and India Navy has also has shown interest for the F-35B
Finland
For the replacement of the F-18C Hornet decision would be taken around 2015
Spain
For the Spanish Navy L 61 Juan Carlos I
Greece
for replacement of the F4E Peace Icarus 2000 and F-16C/D Block 30
















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.png)
.gif)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.gif)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
